Can carbohydrate be reduced too low for weight loss, and glycemic control? Carbohydrate WeightLoss Cardiometabolic Cholesterol Diabetes Diet LipidJournal bswhealth IndianaUniv
By Suchandrima BhowmikFeb 9 2023Reviewed by Danielle Ellis, B.Sc. Carbohydrate-restricted dietary patterns have recently gained popularity for weight loss as well as the management of type 2 diabetes . In addition, recent research has highlighted the improvement in several cardiometabolic risk factors such as hemoglobin A1c , high-density lipoprotein cholesterol , and triglyceride in people who follow a carbohydrate-restricted dietary pattern.
Carbohydrate-restricted dietary patterns, weight loss, and glycemic control Several studies have indicated carbohydrate-restricted dietary patterns to be associated with a decrease in body weight up to 6 months, but no difference was observed at 12 months.
Concerns regarding carbohydrate-restricted dietary patterns One main concern regarding the degree of carbohydrate restriction essential for the production and maintenance of ketosis as well as less severe carbohydrate restriction, is an increase in atherogenic lipoprotein levels, as highlighted by the increase in apolipoprotein B and LDL-C concentrations. LDL-C has been reported to decrease during periods of negative energy balance, which is required for weight loss.
Importance of the quality of foods in healthy dietary patterns Healthcare professionals must give importance to the overall quality of the food as compared to only the quantity of macronutrients. This will help to increase the intake of nutrient-dense foods that provide high-quality protein, carbohydrate, fat, fiber, micronutrients, and bioactive compounds.
Belgique Dernières Nouvelles, Belgique Actualités
Similar News:Vous pouvez également lire des articles d'actualité similaires à celui-ci que nous avons collectés auprès d'autres sources d'information.
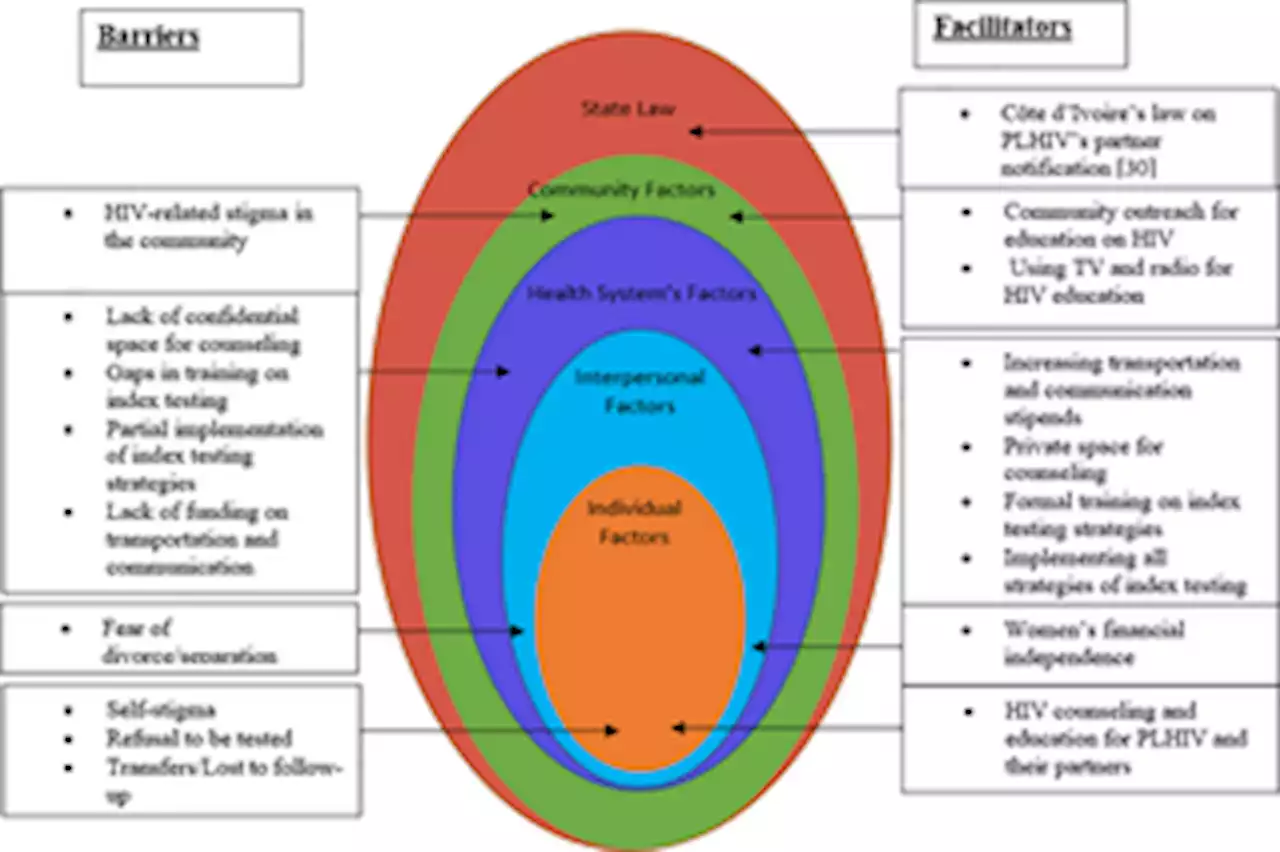 Implementation process and challenges of index testing in Côte d’Ivoire from healthcare workers’ perspectivesA major limiting factor in combatting the HIV epidemic has been the identification of people living with HIV. Index testing programs were developed to face that challenge. Index testing is a focused HIV testing service approach in which family members and partners of people living with HIV are offered testing. Despite the implementation of index testing, there is still a gap between the estimated number of people living with HIV and those who know their status in Côte d’Ivoire. This study aimed to understand the implementation process of index testing in Côte d’Ivoire and to identify implementation challenges from healthcare workers perspectives. In January and February 2020, we conducted a qualitative study through 105 individual semi-structured interviews regarding index testing with clinical providers (physicians, nurses, and midwives) and non-clinical providers (community counselors and their supervisors) at 16 rural health facilities across four regions of Côte d’Ivoire. We asked questions regarding the index testing process, index client intake, contact tracing and testing, the challenges of implementation, and solicited recommendations on improving index testing in Côte d’Ivoire. The interviews revealed that index testing is implemented by non-clinical providers. Passive referral, by which the index client brought their contact to be tested, and providers referral, by which a healthcare worker reached out to the index client’s contact, were the preferred contact tracing and testing strategies. There was not statistically significant difference between immediate and delayed notification. Reported challenges of index testing implementation included index cases refusing to give their partner’s information or a partner refusing to be tested, fear of divorce, societal stigma, long distances, lack of appropriate training in index testing strategies, and lack of a private room for counseling. The recommendations given by providers to combat these was to reinforce HI
Implementation process and challenges of index testing in Côte d’Ivoire from healthcare workers’ perspectivesA major limiting factor in combatting the HIV epidemic has been the identification of people living with HIV. Index testing programs were developed to face that challenge. Index testing is a focused HIV testing service approach in which family members and partners of people living with HIV are offered testing. Despite the implementation of index testing, there is still a gap between the estimated number of people living with HIV and those who know their status in Côte d’Ivoire. This study aimed to understand the implementation process of index testing in Côte d’Ivoire and to identify implementation challenges from healthcare workers perspectives. In January and February 2020, we conducted a qualitative study through 105 individual semi-structured interviews regarding index testing with clinical providers (physicians, nurses, and midwives) and non-clinical providers (community counselors and their supervisors) at 16 rural health facilities across four regions of Côte d’Ivoire. We asked questions regarding the index testing process, index client intake, contact tracing and testing, the challenges of implementation, and solicited recommendations on improving index testing in Côte d’Ivoire. The interviews revealed that index testing is implemented by non-clinical providers. Passive referral, by which the index client brought their contact to be tested, and providers referral, by which a healthcare worker reached out to the index client’s contact, were the preferred contact tracing and testing strategies. There was not statistically significant difference between immediate and delayed notification. Reported challenges of index testing implementation included index cases refusing to give their partner’s information or a partner refusing to be tested, fear of divorce, societal stigma, long distances, lack of appropriate training in index testing strategies, and lack of a private room for counseling. The recommendations given by providers to combat these was to reinforce HI
Lire la suite »
 The effects of a low carbohydrate diet on erectile function and serum testosterone levels in hypogonadal men with metabolic syndrome: a randomized clinical trial - BMC Endocrine DisordersPurpose Metabolic syndrome is a risk factor for several diseases. The relationship between metabolic syndrome and hypogonadism is well known. Our objetive is to assess whether a low carbohydrate diet can increase total serum testosterone and improve erectile function in hypogonadal men with metabolic syndrome. Methods An open label randomized clinical trial was conducted comparing a low carbohydrate diet and controls, during three months, in hypogonadal men with metabolic syndrome. Anthropometric measurements were evaluated as well as total serum testosterone levels, and symptoms of hypogonadism, using the ADAM and AMS scores, and sexual function using IIEF-5 score. Results Eighteen men were evaluated. Anthropometric measures were improved only in low carbohydrate diet group. The intervention group also had a statistically increase in IIEF-5 score and a significant reduction in AMS and ADAM scores (p | 0.001). The increase in serum total testosterone levels was statistically significant in the low carbohydrate group compared to the control group as well as calculated free testosterone (p | 0.001). Conclusions Low carbohydrate diet may increase serum levels of testosterone and improve erectile function in hypogonadal men with metabolic syndrome. However, larger studies are necessary to strongly prove the effectiveness of low carbohydrate diet in treating male hypogonadism.
The effects of a low carbohydrate diet on erectile function and serum testosterone levels in hypogonadal men with metabolic syndrome: a randomized clinical trial - BMC Endocrine DisordersPurpose Metabolic syndrome is a risk factor for several diseases. The relationship between metabolic syndrome and hypogonadism is well known. Our objetive is to assess whether a low carbohydrate diet can increase total serum testosterone and improve erectile function in hypogonadal men with metabolic syndrome. Methods An open label randomized clinical trial was conducted comparing a low carbohydrate diet and controls, during three months, in hypogonadal men with metabolic syndrome. Anthropometric measurements were evaluated as well as total serum testosterone levels, and symptoms of hypogonadism, using the ADAM and AMS scores, and sexual function using IIEF-5 score. Results Eighteen men were evaluated. Anthropometric measures were improved only in low carbohydrate diet group. The intervention group also had a statistically increase in IIEF-5 score and a significant reduction in AMS and ADAM scores (p | 0.001). The increase in serum total testosterone levels was statistically significant in the low carbohydrate group compared to the control group as well as calculated free testosterone (p | 0.001). Conclusions Low carbohydrate diet may increase serum levels of testosterone and improve erectile function in hypogonadal men with metabolic syndrome. However, larger studies are necessary to strongly prove the effectiveness of low carbohydrate diet in treating male hypogonadism.
Lire la suite »
 Exercise Training Is Associated With Treatment Response in... : Official journal of the American College of Gastroenterology | ACGolds of MRI-measured treatment response. METHODS: Randomized controlled trials in adults with NAFLD were identified through March 2022. Exercise training was compared with no exercise training. The primary outcome was ≥30% relative reduction in MRI-measured liver fat (threshold required for histologic improvement in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis activity, nonalcoholic steatohepatitis resolution, and liver fibrosis stage). Different exercise doses were compared. RESULTS: Fourteen studies (551 subjects) met inclusion criteria (mean age 53.3 yrs; body mass index 31.1 kg/m2). Exercise training subjects were more likely to achieve ≥30% relative reduction in MRI-measured liver fat (odds ratio 3.51, 95% confidence interval 1.49–8.23, P=0.004) than those in the control condition. An exercise dose of ≥750 metabolic equivalents of task min/wk (e.g., 150 min/wk of brisk walking) resulted in significant treatment response (MRI response odds ratio 3.73, 95% confidence interval 1.34–10.41, P=0.010), but lesser doses of exercise did not. Treatment response was independent of clinically significant body weight loss (|5%). DISCUSSION: Independent of weight loss, exercise training is 3 and a half times more likely to achieve clinically meaningful treatment response in MRI-measured liver fat compared with standard clinical care. An exercise dose of at least 750 metabolic equivalents of task-min/wk seems required to achieve treatment response. These results further support the weight-neutral benefit of exercise in all patients with NAFLD....
Exercise Training Is Associated With Treatment Response in... : Official journal of the American College of Gastroenterology | ACGolds of MRI-measured treatment response. METHODS: Randomized controlled trials in adults with NAFLD were identified through March 2022. Exercise training was compared with no exercise training. The primary outcome was ≥30% relative reduction in MRI-measured liver fat (threshold required for histologic improvement in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis activity, nonalcoholic steatohepatitis resolution, and liver fibrosis stage). Different exercise doses were compared. RESULTS: Fourteen studies (551 subjects) met inclusion criteria (mean age 53.3 yrs; body mass index 31.1 kg/m2). Exercise training subjects were more likely to achieve ≥30% relative reduction in MRI-measured liver fat (odds ratio 3.51, 95% confidence interval 1.49–8.23, P=0.004) than those in the control condition. An exercise dose of ≥750 metabolic equivalents of task min/wk (e.g., 150 min/wk of brisk walking) resulted in significant treatment response (MRI response odds ratio 3.73, 95% confidence interval 1.34–10.41, P=0.010), but lesser doses of exercise did not. Treatment response was independent of clinically significant body weight loss (|5%). DISCUSSION: Independent of weight loss, exercise training is 3 and a half times more likely to achieve clinically meaningful treatment response in MRI-measured liver fat compared with standard clinical care. An exercise dose of at least 750 metabolic equivalents of task-min/wk seems required to achieve treatment response. These results further support the weight-neutral benefit of exercise in all patients with NAFLD....
Lire la suite »
 Self and caregiver report measurement of sensory features in autism spectrum disorder: a systematic review of psychometric properties - Journal of Neurodevelopmental DisordersBackground Unusual responses to sensory stimuli are considered a diagnostic symptom of autism spectrum disorder with mounting research efforts put towards understanding, characterizing, and treating such symptoms. Methods This paper examines self and caregiver report tools used to measure sensory features in ASD through a systematic review of the psychometric evidence for their use. A total of 31 empirical papers were reviewed across 20 assessment tools. Substantial differences were identified in the specific sensory features defined across assessment tools. Sensory assessment questionnaires were evaluated against quality psychometric evidence criteria to provide a use recommendation. Results Five assessments were identified to be “appropriate with conditions,” while no sensory assessment tools were identified to have sufficient quality psychometric evidence to provide a recommendation of “Appropriate” for measuring sensory features in ASD. Conclusion Evidence from this review highlights potentially significant shortcomings among the current methods used to measure sensory features in ASD and suggests the need for more efforts in developing psychometrically sound sensory assessment tools for use in ASD populations.
Self and caregiver report measurement of sensory features in autism spectrum disorder: a systematic review of psychometric properties - Journal of Neurodevelopmental DisordersBackground Unusual responses to sensory stimuli are considered a diagnostic symptom of autism spectrum disorder with mounting research efforts put towards understanding, characterizing, and treating such symptoms. Methods This paper examines self and caregiver report tools used to measure sensory features in ASD through a systematic review of the psychometric evidence for their use. A total of 31 empirical papers were reviewed across 20 assessment tools. Substantial differences were identified in the specific sensory features defined across assessment tools. Sensory assessment questionnaires were evaluated against quality psychometric evidence criteria to provide a use recommendation. Results Five assessments were identified to be “appropriate with conditions,” while no sensory assessment tools were identified to have sufficient quality psychometric evidence to provide a recommendation of “Appropriate” for measuring sensory features in ASD. Conclusion Evidence from this review highlights potentially significant shortcomings among the current methods used to measure sensory features in ASD and suggests the need for more efforts in developing psychometrically sound sensory assessment tools for use in ASD populations.
Lire la suite »
 Preventing, diagnosing, and treating cardiovascular disease in womenPreventing, diagnosing, and treating cardiovascular disease in women WomensHealth Cardiovascular Disease Cardiology Diet Heart CVD Med_Clinics UPMC BrownUniversity
Preventing, diagnosing, and treating cardiovascular disease in womenPreventing, diagnosing, and treating cardiovascular disease in women WomensHealth Cardiovascular Disease Cardiology Diet Heart CVD Med_Clinics UPMC BrownUniversity
Lire la suite »
