Eyes offer a window into the mystery of humanconsciousness yale NatureComms
A, B). The static noise background appeared continuous from the onset of the pre-stimulus phase through the post-stimulus phase and was then replaced with a solid gray background in the response phase. The target stimulus could appear among one of three opacity conditions: no stimulus or blank , perceptual threshold , and fully opaque . The addition of fully opaque stimuli allowed measurement of participant false negative detection rate.
The center and quadrant location sets defined task-relevant and irrelevant stimulus conditions during the testing phase. In each testing session, participants were instructed that one location set was task-relevant while the other location set was task-irrelevant and testing sessions with different location instructions were conducted on different days. For example, on a day where the center stimuli were task-relevant, they were task-relevant for all trials in the session on that day.
The pre-stimulus, inter-stimulus, and post-stimulus trial phases were jittered intervals between 6 and 10 s during which participants were instructed to maintain fixation at all times . The first and second stimulus phases consisted of a 50 ms stimulus presentation, unless there was a blank presentation when no stimulus appeared. Finally, the response phase was self-paced and presented two sequential questions for stimuli in the task-relevant location set.
After completing all runs of the testing phase, participants were administered a free answer questionnaire that inquired on the general experiences during the study session, including whether if at any time during the testing phase the participants perceived stimuli in the task-irrelevant location set and how the opacity of these stimuli compared to the task-relevant stimuli.
The goal of this questionnaire was to offer a coarse assessment of what participants perceived during the testing phase, particularly for the task-irrelevant stimuli, which would later be used as the basis for a behavioral exclusion criterion for the Report + No-Report Paradigm, although this criterion resulted in no participant exclusions .
Belgique Dernières Nouvelles, Belgique Actualités
Similar News:Vous pouvez également lire des articles d'actualité similaires à celui-ci que nous avons collectés auprès d'autres sources d'information.
 Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli heat-labile toxin drives enteropathic changes in small intestinal epithelia - Nature CommunicationsEnterotoxigenic Escherichia coli infections have been linked to non-diarrheal sequelae however, the reasons for this are unclear. Here, the authors present an additional role of heat-labile toxin in disrupting the structure and function of intestinal epithelial cells.
Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli heat-labile toxin drives enteropathic changes in small intestinal epithelia - Nature CommunicationsEnterotoxigenic Escherichia coli infections have been linked to non-diarrheal sequelae however, the reasons for this are unclear. Here, the authors present an additional role of heat-labile toxin in disrupting the structure and function of intestinal epithelial cells.
Lire la suite »
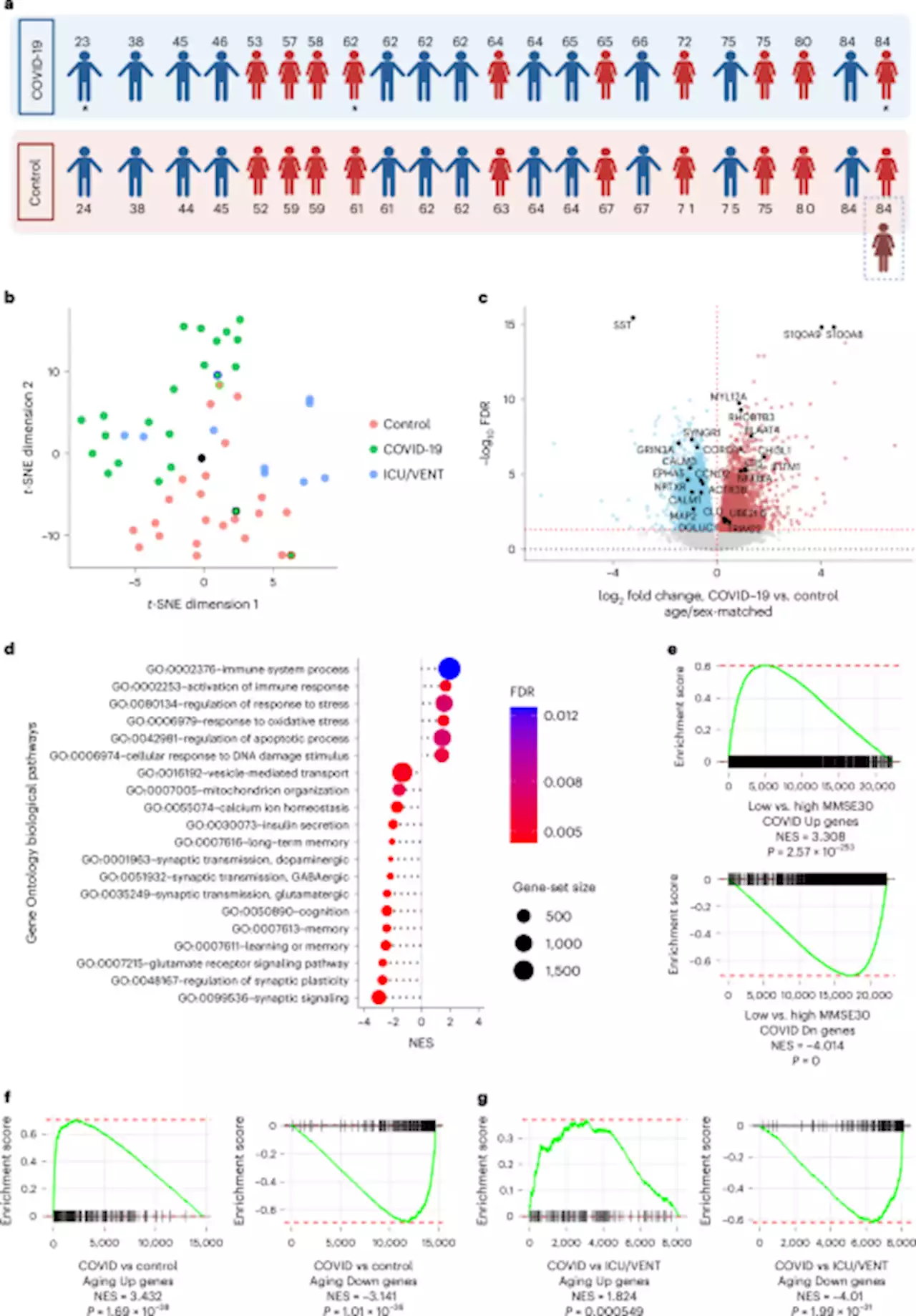 Severe COVID-19 is associated with molecular signatures of aging in the human brain - Nature AgingMavrikaki et al. show that severe COVID-19 is associated with molecular signatures of aging and low cognitive performance in the human frontal cortex; and emphasize the value of neurological follow-up in recovered individuals.
Severe COVID-19 is associated with molecular signatures of aging in the human brain - Nature AgingMavrikaki et al. show that severe COVID-19 is associated with molecular signatures of aging and low cognitive performance in the human frontal cortex; and emphasize the value of neurological follow-up in recovered individuals.
Lire la suite »
 New chatbot has everyone talking to itOpen AI's ChatGPT generates convincing human-like answers in response to human prompts.
New chatbot has everyone talking to itOpen AI's ChatGPT generates convincing human-like answers in response to human prompts.
Lire la suite »
 Dark-field chest X-ray imaging for the assessment of COVID-19-pneumonia - Communications MedicineFrank, Gassert et al. use dark-field chest X-ray imaging to assess COVID-19-pneumonia. Dark-field imaging has a higher sensitivity for COVID-19-pneumonia than attenuation-based imaging and provides an ultralow dose alternative to computed tomography imaging for that purpose.
Dark-field chest X-ray imaging for the assessment of COVID-19-pneumonia - Communications MedicineFrank, Gassert et al. use dark-field chest X-ray imaging to assess COVID-19-pneumonia. Dark-field imaging has a higher sensitivity for COVID-19-pneumonia than attenuation-based imaging and provides an ultralow dose alternative to computed tomography imaging for that purpose.
Lire la suite »
 Use of a glycomics array to establish the anti-carbohydrate antibody repertoire in type 1 diabetes - Nature CommunicationsType I diabetes is characterized by autoantibodies directed against protein or non-protein self-antigens. Here the authors profile glycan reactive anti-carbohydrate antibodies (ACA) in a longitudinal and cross-sectional childhood diabetes cohort and associate clusters of ACA with disease progression.
Use of a glycomics array to establish the anti-carbohydrate antibody repertoire in type 1 diabetes - Nature CommunicationsType I diabetes is characterized by autoantibodies directed against protein or non-protein self-antigens. Here the authors profile glycan reactive anti-carbohydrate antibodies (ACA) in a longitudinal and cross-sectional childhood diabetes cohort and associate clusters of ACA with disease progression.
Lire la suite »
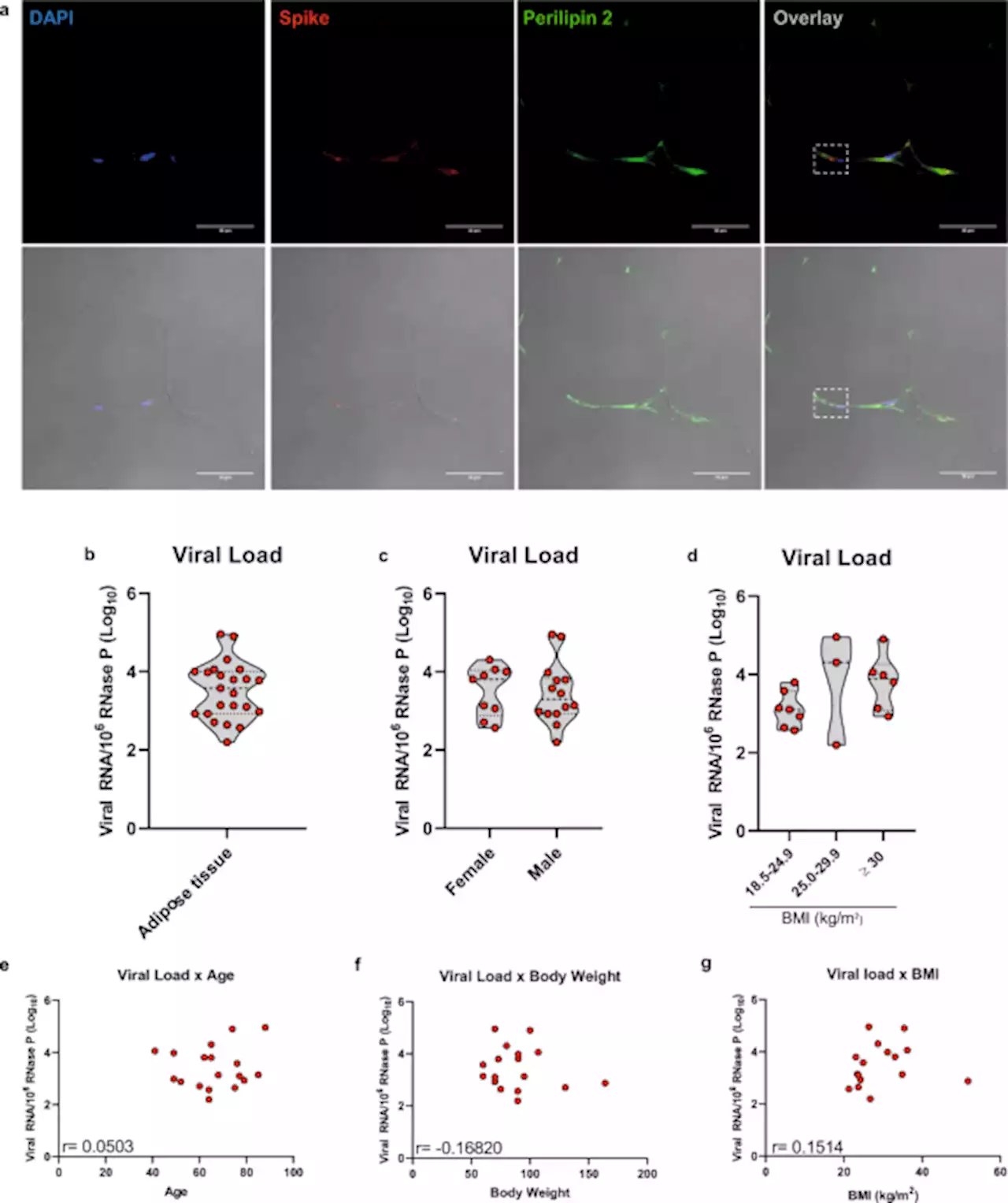 SARS-CoV-2 infects adipose tissue in a fat depot- and viral lineage-dependent manner - Nature CommunicationsVisceral adiposity is a risk factor for severe COVID-19, and infection of adipose tissue by SARS-CoV-2 has been reported. Here the authors confirm that human adipose tissue is a possible site for SARS-CoV-2 infection, but the degree of adipose tissue infection and the way adipocytes respond to the virus depend on the adipose tissue depot and the viral strain.
SARS-CoV-2 infects adipose tissue in a fat depot- and viral lineage-dependent manner - Nature CommunicationsVisceral adiposity is a risk factor for severe COVID-19, and infection of adipose tissue by SARS-CoV-2 has been reported. Here the authors confirm that human adipose tissue is a possible site for SARS-CoV-2 infection, but the degree of adipose tissue infection and the way adipocytes respond to the virus depend on the adipose tissue depot and the viral strain.
Lire la suite »
