An article published in MicrobiomeJ presents NanoPhase: a tool that enables reference-quality genome reconstruction from complex metagenomes directly using only Nanopore long reads. Read the paper here:
c) but only generated half of the flowcell throughput. Therefore, the yield limitation has increased the sequencing cost of the Q20+ chemistry in genome reconstruction at present. In addition, short-read-based Pilon polishing of the MAGs did not considerably improve the genome accuracy , suggesting that it is not an essential step in the future, particularly given the continuous improvement of Nanopore sequencing.
Besides the improved reconstruction of 16S rRNA genes and prediction of secondary metabolites potential discussed in our previous study [], some mobile genetic elements identification that depended heavily on bacterial isolates could also benefit from these high-contiguity reference-quality genomes, e.g., prophage. As a major contributor to the diversity of bacterial gene repertoires, the relationship between bacteria and prophage is multifaceted, i.e.
In addition, the superiority of NanoPhase was also supported by the high IDEEL score, which would further expand its promising application in genome-centric studies, providing a near-complete genomic blueprint and benefiting a finely detailed overview of diverse ecosystems. Currently, NanoPhase also supports genome reconstruction from bacterial isolates and antibiotic resistance genes identification from reconstructed MAGs based on the structured ARG database [].
Although sufficient coverage is vital for the reference-quality genome reconstruction and challenging for most microbial populations in many natural complex communities, we expected that the extraction of ultra-high molecular weight DNA and methylation profiles might further reduce the requirement of sequencing depth and resolve strain-level genome reconstruction.
Belgique Dernières Nouvelles, Belgique Actualités
Similar News:Vous pouvez également lire des articles d'actualité similaires à celui-ci que nous avons collectés auprès d'autres sources d'information.
 Cultivation-independent genomes greatly expand taxonomic-profiling capabilities of mOTUs across various environments - MicrobiomeBackground Taxonomic profiling is a fundamental task in microbiome research that aims to detect and quantify the relative abundance of microorganisms in biological samples. Available methods using shotgun metagenomic data generally depend on the deposition of sequenced and taxonomically annotated genomes, usually from cultures of isolated strains, in reference databases (reference genomes). However, the majority of microorganisms have not been cultured yet. Thus, a substantial fraction of microbial community members remains unaccounted for during taxonomic profiling, particularly in samples from underexplored environments. To address this issue, we developed the mOTU profiler, a tool that enables reference genome-independent species-level profiling of metagenomes. As such, it supports the identification and quantification of both “known” and “unknown” species based on a set of select marker genes. Results We present mOTUs3, a command line tool that enables the profiling of metagenomes for |33,000 species-level operational taxonomic units. To achieve this, we leveraged the reconstruction of |600,000 draft genomes, most of which are metagenome-assembled genomes (MAGs), from diverse microbiomes, including soil, freshwater systems, and the gastrointestinal tract of ruminants and other animals, which we found to be underrepresented by reference genomes. Overall, two thirds of all species-level taxa lacked a reference genome. The cumulative relative abundance of these newly included taxa was low in well-studied microbiomes, such as the human body sites (6–11%). By contrast, they accounted for substantial proportions (ocean, freshwater, soil: 43–63%) or even the majority (pig, fish, cattle: 60–80%) of the relative abundance across diverse non-human-associated microbiomes. Using community-developed benchmarks and datasets, we found mOTUs3 to be more accurate than other methods and to be more congruent with 16S rRNA gene-based methods for taxonomic profiling. Furthermore, we
Cultivation-independent genomes greatly expand taxonomic-profiling capabilities of mOTUs across various environments - MicrobiomeBackground Taxonomic profiling is a fundamental task in microbiome research that aims to detect and quantify the relative abundance of microorganisms in biological samples. Available methods using shotgun metagenomic data generally depend on the deposition of sequenced and taxonomically annotated genomes, usually from cultures of isolated strains, in reference databases (reference genomes). However, the majority of microorganisms have not been cultured yet. Thus, a substantial fraction of microbial community members remains unaccounted for during taxonomic profiling, particularly in samples from underexplored environments. To address this issue, we developed the mOTU profiler, a tool that enables reference genome-independent species-level profiling of metagenomes. As such, it supports the identification and quantification of both “known” and “unknown” species based on a set of select marker genes. Results We present mOTUs3, a command line tool that enables the profiling of metagenomes for |33,000 species-level operational taxonomic units. To achieve this, we leveraged the reconstruction of |600,000 draft genomes, most of which are metagenome-assembled genomes (MAGs), from diverse microbiomes, including soil, freshwater systems, and the gastrointestinal tract of ruminants and other animals, which we found to be underrepresented by reference genomes. Overall, two thirds of all species-level taxa lacked a reference genome. The cumulative relative abundance of these newly included taxa was low in well-studied microbiomes, such as the human body sites (6–11%). By contrast, they accounted for substantial proportions (ocean, freshwater, soil: 43–63%) or even the majority (pig, fish, cattle: 60–80%) of the relative abundance across diverse non-human-associated microbiomes. Using community-developed benchmarks and datasets, we found mOTUs3 to be more accurate than other methods and to be more congruent with 16S rRNA gene-based methods for taxonomic profiling. Furthermore, we
Lire la suite »
 Bill Foley completes Bournemouth takeoverBill Foley has completed his takeover of AFC Bournemouth from previous owner Maxim Denim after the transaction received all necessary approvals from the Premier League. Foley, 77, also has an extensive background in sports including success as the founder and owner of the National Hockey League’s...
Bill Foley completes Bournemouth takeoverBill Foley has completed his takeover of AFC Bournemouth from previous owner Maxim Denim after the transaction received all necessary approvals from the Premier League. Foley, 77, also has an extensive background in sports including success as the founder and owner of the National Hockey League’s...
Lire la suite »
 Increased serum homocysteine in first episode and drug-naïve individuals with schizophrenia: sex differences and correlations with clinical symptoms - BMC PsychiatryBackground Accumulating evidence shows that homocysteine (Hcy) is implicated in the pathophysiology of schizophrenia, and plays an important role in clinical characteristics. This study evaluated the relationships between Hcy levels and clinical features in first-episode, Chinese Han, drug-naïve (FEDN) patients with schizophrenia. Methods FEDN individuals (119 with schizophrenia and 81 healthy controls matched for age, sex, education, and body mass index (BMI)) were enrolled. The serum Hcy levels were determined by enzyme cycle assay experiments. Severities of clinical symptoms were rated on the Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale (PANSS). Results FEDN individuals with schizophrenia had higher Hcy levels compared with healthy controls (F = 46.865, P 0.05). Male individuals had significantly higher serum Hcy levels than female individuals (F = 7.717, P = 0.006) after controlling for confounding factors (F = 0.759, P = 0.011). Conclusions Serum Hcy levels were increased in FEDN individuals with schizophrenia, and Hcy levels may be involved in pathophysiological mechanisms. Sex differences in Hcy levels were observed, with higher levels in male FEDN individuals compared to females.
Increased serum homocysteine in first episode and drug-naïve individuals with schizophrenia: sex differences and correlations with clinical symptoms - BMC PsychiatryBackground Accumulating evidence shows that homocysteine (Hcy) is implicated in the pathophysiology of schizophrenia, and plays an important role in clinical characteristics. This study evaluated the relationships between Hcy levels and clinical features in first-episode, Chinese Han, drug-naïve (FEDN) patients with schizophrenia. Methods FEDN individuals (119 with schizophrenia and 81 healthy controls matched for age, sex, education, and body mass index (BMI)) were enrolled. The serum Hcy levels were determined by enzyme cycle assay experiments. Severities of clinical symptoms were rated on the Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale (PANSS). Results FEDN individuals with schizophrenia had higher Hcy levels compared with healthy controls (F = 46.865, P 0.05). Male individuals had significantly higher serum Hcy levels than female individuals (F = 7.717, P = 0.006) after controlling for confounding factors (F = 0.759, P = 0.011). Conclusions Serum Hcy levels were increased in FEDN individuals with schizophrenia, and Hcy levels may be involved in pathophysiological mechanisms. Sex differences in Hcy levels were observed, with higher levels in male FEDN individuals compared to females.
Lire la suite »
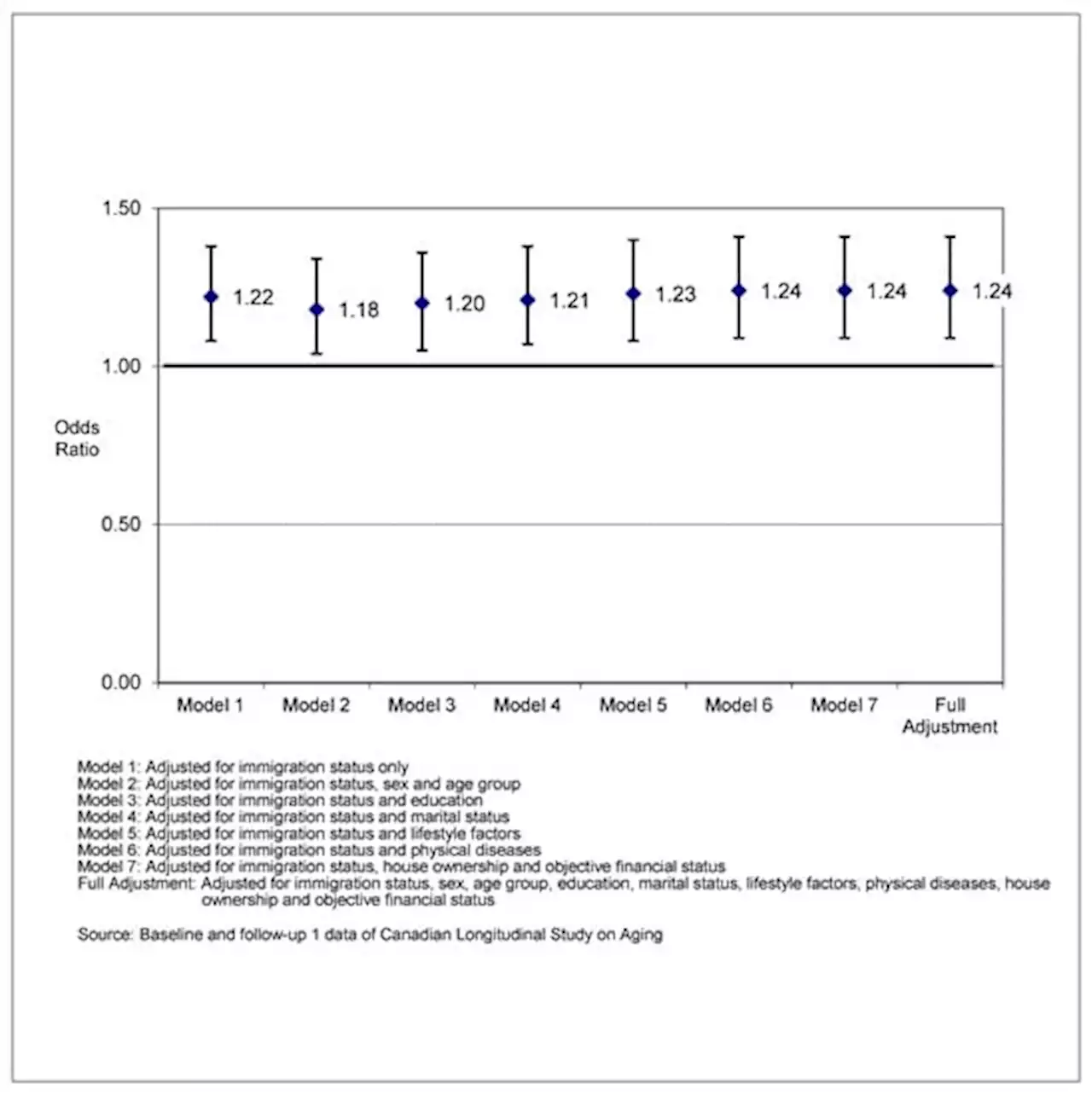 Successful Aging among Immigrant and Canadian-Born Older Adults: Findings from the Canadian Longitudinal Study on Aging (CLSA)Background: Few studies in Canada have focused on the relationship between immigrant status and successful aging. The concept of successful aging used in this study includes the ability to accomplish both activities of daily living (ADLs) and instrumental activities of daily living (IADLs), freedom from mental illness, memory problems and disabling chronic pain, adequate social support and older adults’ self-reported happiness and subjective perception of their physical health, mental health and aging process as good. Methods: The present study analyzed the first two waves of data from the comprehensive cohort of the Canadian Longitudinal Study on Aging (CLSA). The sample includes 7651 respondents aged 60+ at time 2, of whom 1446 respondents were immigrants. Bivariate and multivariable binary logistic regression analyses were conducted. Results: Canadian-born older adults had a slightly higher prevalence and age-sex adjusted odds of achieving successful aging than their immigrant counterparts (aOR=1.18, 95% CI: 1.04, 1.34, p < 0.001). After adjusting for 18 additional factors, immigrant status remained statistically significant (aOR=1.24, 95% CI: 1.09, 1.41, p < 0.001). Significant baseline factors associated with successful aging among immigrants included being younger, having higher income, being married, not being obese, never smoking, engaging in moderate or strenuous physical activities, not having sleeping problems and being free of heart disease or arthritis. Conclusions: Immigrant older adults had a lower prevalence of successful aging than their Canadian-born peers. Further research could investigate whether policies and interventions supporting older immigrants and promoting a healthy lifestyle enhance older adults achieve successful aging in later life.
Successful Aging among Immigrant and Canadian-Born Older Adults: Findings from the Canadian Longitudinal Study on Aging (CLSA)Background: Few studies in Canada have focused on the relationship between immigrant status and successful aging. The concept of successful aging used in this study includes the ability to accomplish both activities of daily living (ADLs) and instrumental activities of daily living (IADLs), freedom from mental illness, memory problems and disabling chronic pain, adequate social support and older adults’ self-reported happiness and subjective perception of their physical health, mental health and aging process as good. Methods: The present study analyzed the first two waves of data from the comprehensive cohort of the Canadian Longitudinal Study on Aging (CLSA). The sample includes 7651 respondents aged 60+ at time 2, of whom 1446 respondents were immigrants. Bivariate and multivariable binary logistic regression analyses were conducted. Results: Canadian-born older adults had a slightly higher prevalence and age-sex adjusted odds of achieving successful aging than their immigrant counterparts (aOR=1.18, 95% CI: 1.04, 1.34, p < 0.001). After adjusting for 18 additional factors, immigrant status remained statistically significant (aOR=1.24, 95% CI: 1.09, 1.41, p < 0.001). Significant baseline factors associated with successful aging among immigrants included being younger, having higher income, being married, not being obese, never smoking, engaging in moderate or strenuous physical activities, not having sleeping problems and being free of heart disease or arthritis. Conclusions: Immigrant older adults had a lower prevalence of successful aging than their Canadian-born peers. Further research could investigate whether policies and interventions supporting older immigrants and promoting a healthy lifestyle enhance older adults achieve successful aging in later life.
Lire la suite »
 “My Hand Is Different”: Altered Body Perception in Stroke Survivors with Chronic PainBackground: Chronic pain and body perception disturbance are common following stroke. It is possible that an interaction exists between pain and body perception disturbance, and that a change in one may influence the other. We therefore investigated the presence of body perception disturbance in individuals with stroke, aiming to determine if a perceived change in hand size contralateral to the stroke lesion is more common in those with chronic pain than in those without. Methods: Stroke survivors (N=523) completed an online survey that included: stroke details, pain features, and any difference in perceived hand size post-stroke. Results: Individuals with stroke who experienced chronic pain were almost three times as likely as those without chronic pain to perceive their hand as now being a different size (OR=2.895; 95%CI 1.844, 4.547). Further, those with chronic pain whose pain included the hand were almost twice as likely to perceive altered hand size than those whose pain did not include the hand (OR=1.862; 95%CI 1.170, 2.962). This was not influenced by hemisphere of lesion (p=0.190). Conclusions: The results point to a new characteristic of chronic pain in stroke, raising the possibility of body perception disturbance being a rehabilitation target to improve function and pain-related outcomes for stroke survivors.
“My Hand Is Different”: Altered Body Perception in Stroke Survivors with Chronic PainBackground: Chronic pain and body perception disturbance are common following stroke. It is possible that an interaction exists between pain and body perception disturbance, and that a change in one may influence the other. We therefore investigated the presence of body perception disturbance in individuals with stroke, aiming to determine if a perceived change in hand size contralateral to the stroke lesion is more common in those with chronic pain than in those without. Methods: Stroke survivors (N=523) completed an online survey that included: stroke details, pain features, and any difference in perceived hand size post-stroke. Results: Individuals with stroke who experienced chronic pain were almost three times as likely as those without chronic pain to perceive their hand as now being a different size (OR=2.895; 95%CI 1.844, 4.547). Further, those with chronic pain whose pain included the hand were almost twice as likely to perceive altered hand size than those whose pain did not include the hand (OR=1.862; 95%CI 1.170, 2.962). This was not influenced by hemisphere of lesion (p=0.190). Conclusions: The results point to a new characteristic of chronic pain in stroke, raising the possibility of body perception disturbance being a rehabilitation target to improve function and pain-related outcomes for stroke survivors.
Lire la suite »
 Solitary and multiple thyroid nodules as predictors of malignancy: a systematic review and meta-analysis - Thyroid ResearchBackground The debate on whether or not there is a difference in the incidence of thyroid cancer between the patients with Solitary thyroid Nodule (STN) and Multinodular Goiter (MNG) has been constantly present for the last few decades. With newer studies yielding mixed results, it was imperative to systematically compile all available literature on the topic. Methods PubMed/MEDLINE, Cochrane Central, ScienceDirect, GoogleScholar, International Clinical Trials registry, and reference lists of the included articles were systematically searched for article retrieval. No filter was applied in terms of time, study design, language or country of publication. Rigorous screening as per PRISMA guidelines was undertaken by 2 independent reviewers in order to identify the articles that were most relevant to the topic. Results Twenty-two studies spanning from 1992 to 2018 were included in this analysis and encompassed 50,321 patients, 44.2% of which belonged to the STN subgroup and 55.37% to the MNG subgroup. MNG was found to be associated with a significantly lower risk of thyroid cancer (OR = 0.76; 95% CI 0.61–0.96) when compared with STN. Papillary carcinoma was the most frequently occurring carcinoma across both groups, followed by follicular and medullary carcinomas. A subgroup analysis was performed to assess the efficacy of the two most commonly employed diagnostic tools i.e. surgery and fine needle aspiration cytology (FNAC), however it yielded nonsignificant results, indicating a comparable usefulness of the two. Another subgroup analysis run on the basis of the presumed iodine status of the participants also yielded nonsignificant results. Conclusion There is a higher incidence of thyroid cancer among patients of STN, however, given the low quality of existing evidence on the topic, it is crucial to conduct larger studies that can establish association with a greater precision.
Solitary and multiple thyroid nodules as predictors of malignancy: a systematic review and meta-analysis - Thyroid ResearchBackground The debate on whether or not there is a difference in the incidence of thyroid cancer between the patients with Solitary thyroid Nodule (STN) and Multinodular Goiter (MNG) has been constantly present for the last few decades. With newer studies yielding mixed results, it was imperative to systematically compile all available literature on the topic. Methods PubMed/MEDLINE, Cochrane Central, ScienceDirect, GoogleScholar, International Clinical Trials registry, and reference lists of the included articles were systematically searched for article retrieval. No filter was applied in terms of time, study design, language or country of publication. Rigorous screening as per PRISMA guidelines was undertaken by 2 independent reviewers in order to identify the articles that were most relevant to the topic. Results Twenty-two studies spanning from 1992 to 2018 were included in this analysis and encompassed 50,321 patients, 44.2% of which belonged to the STN subgroup and 55.37% to the MNG subgroup. MNG was found to be associated with a significantly lower risk of thyroid cancer (OR = 0.76; 95% CI 0.61–0.96) when compared with STN. Papillary carcinoma was the most frequently occurring carcinoma across both groups, followed by follicular and medullary carcinomas. A subgroup analysis was performed to assess the efficacy of the two most commonly employed diagnostic tools i.e. surgery and fine needle aspiration cytology (FNAC), however it yielded nonsignificant results, indicating a comparable usefulness of the two. Another subgroup analysis run on the basis of the presumed iodine status of the participants also yielded nonsignificant results. Conclusion There is a higher incidence of thyroid cancer among patients of STN, however, given the low quality of existing evidence on the topic, it is crucial to conduct larger studies that can establish association with a greater precision.
Lire la suite »