PARK2 duplication or microdeletion and neurological diseases PARK2 CGH microdeletion microduplication neurodevelopmental neurology parkinsons ADHD Genes_MDPI UR_Med
The Parkinson's disease 2 gene encodes a protein with ubiquitin-E3-ligase activity, which has been identified as a p53 transcriptional repressor. The primary function of the Parkin protein is to control programmed cell death and mitophagy. This protein is expressed in various nervous system regions, including the basal ganglia, cerebellum, and cerebral cortex.
About the study In the present study, researchers at the University of Rochester Medical Center in the United States presented a series of patients with duplication/deletion at the 6q26 locus. Results The team discovered approximately nine patients in the study database whose aCGH tests revealed aberrations in the PARK2 gene copy number. The first patient was a nine-year-old girl with a history of seizures, developmental delay, encephalopathy, and dysmorphic features. Array CGH assessment revealed that the first patient had duplications of 506 Kb and 347 kb at chromosome 17q21.3–17q21.32 and chromosome 6q26 region containing the PARK2 gene, respectively. The chromosome 17q21.3–17q21.
Antibodies eBook Compilation of the top interviews, articles, and news in the last year. Download a free copy The second patient was a one-year-old boy referred for Dandy-Walker disease and hypotonia. He displayed a duplication of 726 Kb on the chromosome 6q26 region containing the PACRG and PARK2 genes, as revealed by array CGH analysis. FISH studies of parental samples noted maternal inheritance. The third patient was a one-day-old fetus that died immediately after birth.
Belgique Dernières Nouvelles, Belgique Actualités
Similar News:Vous pouvez également lire des articles d'actualité similaires à celui-ci que nous avons collectés auprès d'autres sources d'information.
 New Parkinson's drug and statins among medicines unlocked for Northern Ireland by Brexit dealThanks to the new Windsor Framework, almost every concern over GB to NI medicines supply has been resolved according to health experts who said the deal went beyond their expectations in solving potential long-term problems 🔎 Analysis from PMGallagher1
New Parkinson's drug and statins among medicines unlocked for Northern Ireland by Brexit dealThanks to the new Windsor Framework, almost every concern over GB to NI medicines supply has been resolved according to health experts who said the deal went beyond their expectations in solving potential long-term problems 🔎 Analysis from PMGallagher1
Lire la suite »
 Children's bad dreams linked to a higher risk of dementia and Parkinson's disease in adulthood, finds new studyCan children's dreams foretell events that will happen nearly 40 years into the future? Yes, according to the results of my latest study published in the journal eClinicalMedicine.
Children's bad dreams linked to a higher risk of dementia and Parkinson's disease in adulthood, finds new studyCan children's dreams foretell events that will happen nearly 40 years into the future? Yes, according to the results of my latest study published in the journal eClinicalMedicine.
Lire la suite »
 ShrinkCRISPR: a flexible method for differential fitness analysis of CRISPR-Cas9 screen data - BMC BioinformaticsBackground CRISPR screens provide large-scale assessment of cellular gene functions. Pooled libraries typically consist of several single guide RNAs (sgRNAs) per gene, for a large number of genes, which are transduced in such a way that every cell receives at most one sgRNA, resulting in the disruption of a single gene in that cell. This approach is often used to investigate effects on cellular fitness, by measuring sgRNA abundance at different time points. Comparing gene knockout effects between different cell populations is challenging due to variable cell-type specific parameters and between replicates variation. Failure to take those into account can lead to inflated or false discoveries. Results We propose a new, flexible approach called ShrinkCRISPR that can take into account multiple sources of variation. Impact on cellular fitness between conditions is inferred by using a mixed-effects model, which allows to test for gene-knockout effects while taking into account sgRNA-specific variation. Estimates are obtained using an empirical Bayesian approach. ShrinkCRISPR can be applied to a variety of experimental designs, including multiple factors. In simulation studies, we compared ShrinkCRISPR results with those of drugZ and MAGeCK, common methods used to detect differential effect on cell fitness. ShrinkCRISPR yielded as many true discoveries as drugZ using a paired screen design, and outperformed both drugZ and MAGeCK for an independent screen design. Although conservative, ShrinkCRISPR was the only approach that kept false discoveries under control at the desired level, for both designs. Using data from several publicly available screens, we showed that ShrinkCRISPR can take data for several time points into account simultaneously, helping to detect early and late differential effects. Conclusions ShrinkCRISPR is a robust and flexible approach, able to incorporate different sources of variations and to test for differential effect on cell fitness at the gene l
ShrinkCRISPR: a flexible method for differential fitness analysis of CRISPR-Cas9 screen data - BMC BioinformaticsBackground CRISPR screens provide large-scale assessment of cellular gene functions. Pooled libraries typically consist of several single guide RNAs (sgRNAs) per gene, for a large number of genes, which are transduced in such a way that every cell receives at most one sgRNA, resulting in the disruption of a single gene in that cell. This approach is often used to investigate effects on cellular fitness, by measuring sgRNA abundance at different time points. Comparing gene knockout effects between different cell populations is challenging due to variable cell-type specific parameters and between replicates variation. Failure to take those into account can lead to inflated or false discoveries. Results We propose a new, flexible approach called ShrinkCRISPR that can take into account multiple sources of variation. Impact on cellular fitness between conditions is inferred by using a mixed-effects model, which allows to test for gene-knockout effects while taking into account sgRNA-specific variation. Estimates are obtained using an empirical Bayesian approach. ShrinkCRISPR can be applied to a variety of experimental designs, including multiple factors. In simulation studies, we compared ShrinkCRISPR results with those of drugZ and MAGeCK, common methods used to detect differential effect on cell fitness. ShrinkCRISPR yielded as many true discoveries as drugZ using a paired screen design, and outperformed both drugZ and MAGeCK for an independent screen design. Although conservative, ShrinkCRISPR was the only approach that kept false discoveries under control at the desired level, for both designs. Using data from several publicly available screens, we showed that ShrinkCRISPR can take data for several time points into account simultaneously, helping to detect early and late differential effects. Conclusions ShrinkCRISPR is a robust and flexible approach, able to incorporate different sources of variations and to test for differential effect on cell fitness at the gene l
Lire la suite »
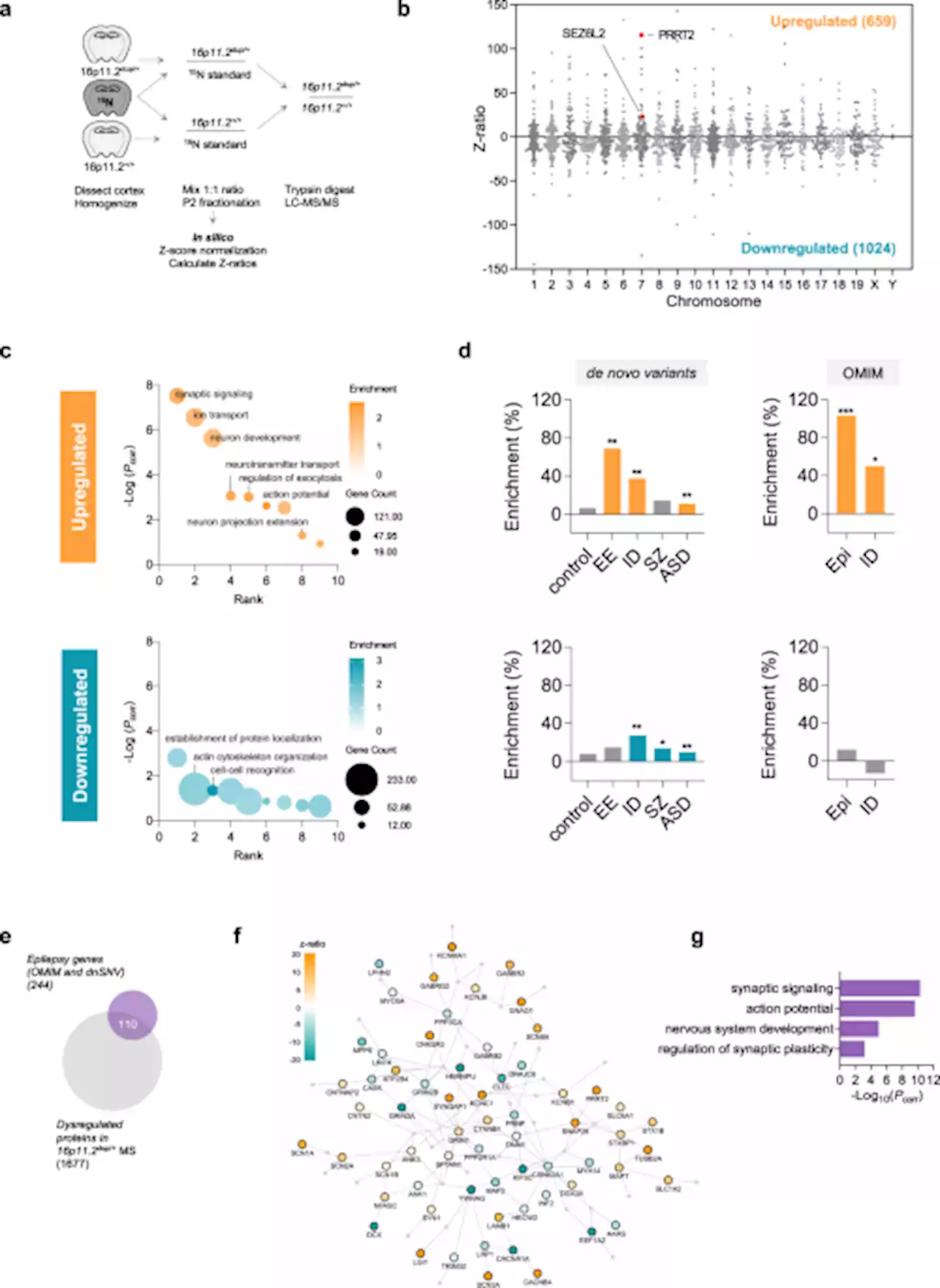 Rescue of neuropsychiatric phenotypes in a mouse model of 16p11.2 duplication syndrome by genetic correction of an epilepsy network hub - Nature CommunicationsThe 16p11.2 duplication confers risk for autism and schizophrenia, but the disease mechanisms are unknown. Here, the authors use proteomics to show dysregulation of synaptic and epilepsy-associated protein networks in the cortex of model mice, and demonstrate that correcting Prrt2 gene dosage rescues circuit hypersynchrony and behavioural phenotypes.
Rescue of neuropsychiatric phenotypes in a mouse model of 16p11.2 duplication syndrome by genetic correction of an epilepsy network hub - Nature CommunicationsThe 16p11.2 duplication confers risk for autism and schizophrenia, but the disease mechanisms are unknown. Here, the authors use proteomics to show dysregulation of synaptic and epilepsy-associated protein networks in the cortex of model mice, and demonstrate that correcting Prrt2 gene dosage rescues circuit hypersynchrony and behavioural phenotypes.
Lire la suite »
 How a healthy heart can slash your risk for 4 killer diseases - 5 tips to protect your tickerA HEALTHY heart can add almost a decade to your life, new research has shown. Keeping your ticker in good nick increases your chances of avoiding four major killers, scientists in the US found. The…
How a healthy heart can slash your risk for 4 killer diseases - 5 tips to protect your tickerA HEALTHY heart can add almost a decade to your life, new research has shown. Keeping your ticker in good nick increases your chances of avoiding four major killers, scientists in the US found. The…
Lire la suite »
 Importance of Research into Rare DiseaseAccording to Global Genes, around 7,000 rarediseases affect approximately 350 million people worldwide. Read more about the importance of research into rare diseases here: raredisease RareDiseaseDay RareDiseaseDay2023 rarediseaseday
Importance of Research into Rare DiseaseAccording to Global Genes, around 7,000 rarediseases affect approximately 350 million people worldwide. Read more about the importance of research into rare diseases here: raredisease RareDiseaseDay RareDiseaseDay2023 rarediseaseday
Lire la suite »
