Prior infection and vaccination protects against severe outcomes from SARS-CoV-2 Omicron infection Coronavirus Disease COVID Omicron SARSCoV2 JIDJournal UNC ClevelandClinic
By Nidhi Saha, BDSDec 1 2022Reviewed by Benedette Cuffari, M.Sc. A new study published in The Journal of Infectious Diseases reports that both previous infections with the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 and booster vaccination protect against intensive care unit admission and mortality following infection with the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant. However, the extent of this protection is reduced against the Omicron variant compared to the Delta variant.
Genetics & Genomics eBook Compilation of the top interviews, articles, and news in the last year. Download a copy today This has resulted in the emergence of different viral variants with properties distinct from the original SARS-CoV-2 strain. To date, five major SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern have been identified, which include the Alpha , Beta , Gamma , Delta , and Omicron variants.
Delta variants were used in this study as controls to determine whether immunization, prior infection and therapy protect against infection from the Omicron VOC and its severe outcomes, as well as the lethality of Omicron infections. The researchers used logistic and Cox regression analyses to assess whether vaccination, prior infection and/or monoclonal antibody therapy correlate with the risks of prolonged hospitalization and death in ICUs.
Delta variant causes more severe disease than Omicron During the Omicron-predominant period, Kaplan-Meier estimates of survival probabilities were significantly higher than those during the Delta-predominant period. The 28-day mortality rates were 1% and 1.80%, respectively, and the hazard ratio for death due to Omicron versus Delta infection was 0.60.
Belgique Dernières Nouvelles, Belgique Actualités
Similar News:Vous pouvez également lire des articles d'actualité similaires à celui-ci que nous avons collectés auprès d'autres sources d'information.
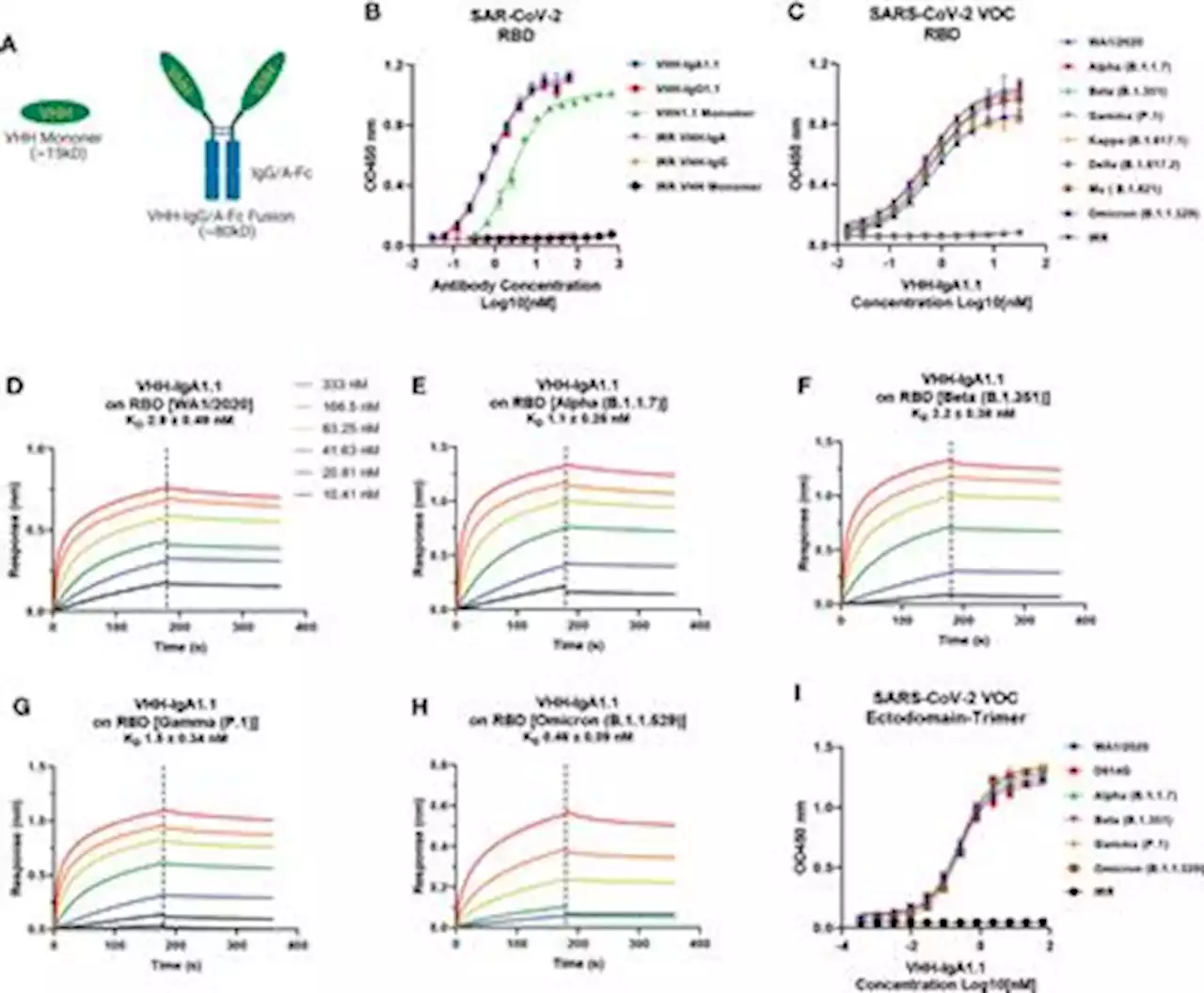 Frontiers | Mucosal nanobody IgA as inhalable and affordable prophylactic and therapeutic treatment against SARS-CoV-2 and emerging variantsAnti-COVID antibody therapeutics have been developed but not widely used due to their high cost and escape of neutralization from the emerging variants. Here, we describe the development of VHH1.1, a nanobody IgA fusion molecular as an inhalable, affordable and less invasive prophylactic and therapeutic treatment against SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variants. VHH-IgA 1.1 recognizes a conserved epitope of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein Receptor Binding Domain (RBD) and potently neutralizes major global SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern (VOC) including the Omicron variant and its sub lineages BA.1.1, BA.2 and BA.2.12.1. The IgA fusion of VHH1.1 is also much more potent against Omicron variants as compared to its IgG Fc fusion demonstrating the importance of IgA mediated mucosal protection for Omicron infection. Intranasal administration of VHH-IgA1.1 prior to or after challenge conferred significant protection from severe respiratory disease in K18-ACE2 transgenic mice infected with SARS-CoV-2 VOC. More importantly, for cost-effective production, VHH-IgA1.1 produced in Pichia pastoris had comparable potency as mammalian produced antibody. Our study demonstrates that intranasal administration of VHH-IgA fusion protein produced affordably provides effective mucosal immunity against infection of SARS-CoV-2 including the emerging variants.
Frontiers | Mucosal nanobody IgA as inhalable and affordable prophylactic and therapeutic treatment against SARS-CoV-2 and emerging variantsAnti-COVID antibody therapeutics have been developed but not widely used due to their high cost and escape of neutralization from the emerging variants. Here, we describe the development of VHH1.1, a nanobody IgA fusion molecular as an inhalable, affordable and less invasive prophylactic and therapeutic treatment against SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variants. VHH-IgA 1.1 recognizes a conserved epitope of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein Receptor Binding Domain (RBD) and potently neutralizes major global SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern (VOC) including the Omicron variant and its sub lineages BA.1.1, BA.2 and BA.2.12.1. The IgA fusion of VHH1.1 is also much more potent against Omicron variants as compared to its IgG Fc fusion demonstrating the importance of IgA mediated mucosal protection for Omicron infection. Intranasal administration of VHH-IgA1.1 prior to or after challenge conferred significant protection from severe respiratory disease in K18-ACE2 transgenic mice infected with SARS-CoV-2 VOC. More importantly, for cost-effective production, VHH-IgA1.1 produced in Pichia pastoris had comparable potency as mammalian produced antibody. Our study demonstrates that intranasal administration of VHH-IgA fusion protein produced affordably provides effective mucosal immunity against infection of SARS-CoV-2 including the emerging variants.
Lire la suite »
 The evolutionary trajectories and mechanisms driving the emergence of post-Omicron SARS-CoV-2 lineagesThe evolutionary trajectories and mechanisms driving the emergence of post-Omicron SARS-CoV-2 lineages COVID19 coronavirus covid SARSCoV2 evolution
The evolutionary trajectories and mechanisms driving the emergence of post-Omicron SARS-CoV-2 lineagesThe evolutionary trajectories and mechanisms driving the emergence of post-Omicron SARS-CoV-2 lineages COVID19 coronavirus covid SARSCoV2 evolution
Lire la suite »
 Plasma from vaccinated and COVID-19 convalescent subjects as passive immunotherapy against the new Omicron BQ.1.1, XBB, and BF.7 variantsPlasma from vaccinated and COVID-19 convalescent subjects as passive immunotherapy against the new Omicron BQ.1.1, XBB, and BF.7 variants biorxivpreprint JohnsHopkinsSPH COVID19 vaccinated covid coronavirus Omicron
Plasma from vaccinated and COVID-19 convalescent subjects as passive immunotherapy against the new Omicron BQ.1.1, XBB, and BF.7 variantsPlasma from vaccinated and COVID-19 convalescent subjects as passive immunotherapy against the new Omicron BQ.1.1, XBB, and BF.7 variants biorxivpreprint JohnsHopkinsSPH COVID19 vaccinated covid coronavirus Omicron
Lire la suite »
 Benefits of an original booster dose against omicron may be affected by prior SARS-CoV-2 infectionmRNA COVID-19 vaccines are less effective against omicron infections than other variants. A study published December 1 in the open access journal PLOS Medicine by Margaret L. Lind at the Yale School of Public Health and colleagues suggests that the additional protection offered by the initial booster shot may be reduced among people with a previous COVID-19 infection.
Benefits of an original booster dose against omicron may be affected by prior SARS-CoV-2 infectionmRNA COVID-19 vaccines are less effective against omicron infections than other variants. A study published December 1 in the open access journal PLOS Medicine by Margaret L. Lind at the Yale School of Public Health and colleagues suggests that the additional protection offered by the initial booster shot may be reduced among people with a previous COVID-19 infection.
Lire la suite »
 Risk factor assessment for the development of severe SARS-CoV-2 breakthrough infectionsresearchers evaluated the severity of breakthrough SARS-CoV-2 (severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2) infections and the risk factors associated with severity among individuals vaccinated for coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in Sousse, Tunisia.
Risk factor assessment for the development of severe SARS-CoV-2 breakthrough infectionsresearchers evaluated the severity of breakthrough SARS-CoV-2 (severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2) infections and the risk factors associated with severity among individuals vaccinated for coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in Sousse, Tunisia.
Lire la suite »
 Researchers explore failed SARS-CoV-2 screening at hospital entrancesResearchers evaluated the failure rates of COVID-19 screening at hospital entrances for visitors, health professionals, and patients at the Yale New Haven Hospital in the US.
Researchers explore failed SARS-CoV-2 screening at hospital entrancesResearchers evaluated the failure rates of COVID-19 screening at hospital entrances for visitors, health professionals, and patients at the Yale New Haven Hospital in the US.
Lire la suite »
