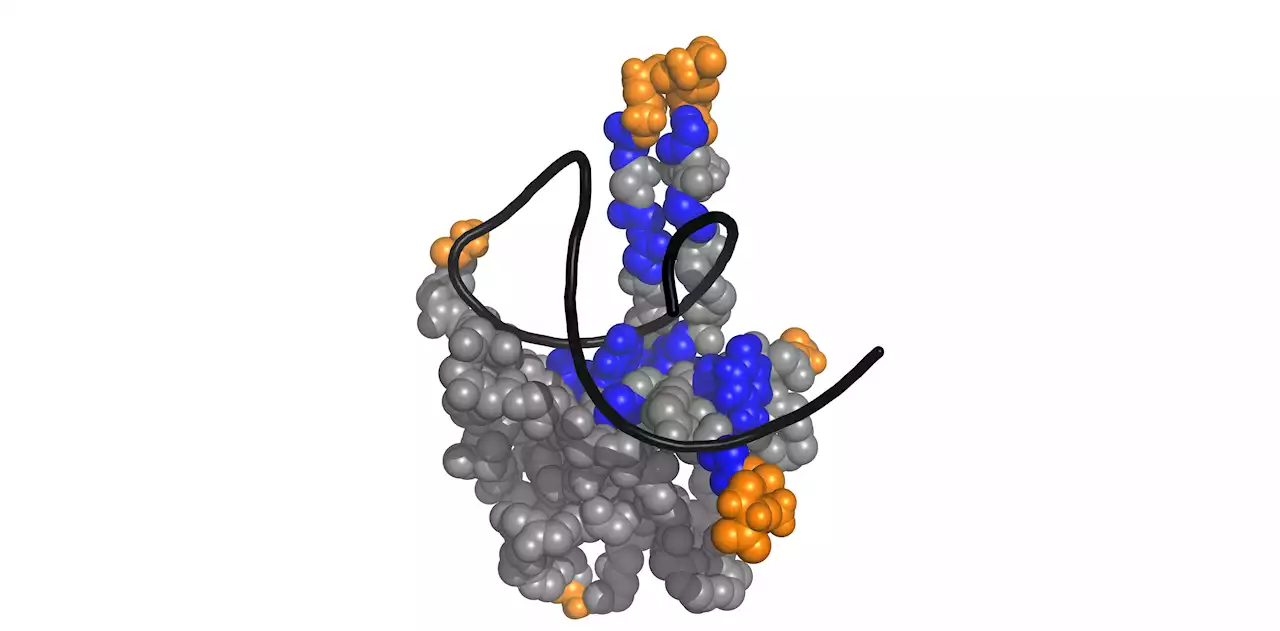
Immediately after the infection of a cell in the throat or lungs, the SARS-CoV-2 virus works very hard to replicate, using the human cell's metabolic pathways to produce its proteins and make sure that its genetic material (the RNA genome) is copied. The RNA genome is then packaged very compactly into new virus particles that are released from the cell to infect more cells.
, called the nucleocapsid protein , is particularly important for rapid and efficient replication. It wraps around the RNA genome in the virus and ensures that the very long RNA is tightly coiled up. When it penetrates the cell, N detaches itself from the RNA genome and assumes a whole range of functions duringWhen the RNA is translated into viral proteins, N protects the RNA from being destroyed by the cell's antiviral defense mechanism .
Like a Swiss army knife, N has several tools at its disposal for all these functions: Firstly, N must be able to distinguish between cellular and viral RNA and to coil up the latter in a spiral shape. That is why N can bind viral RNA in a relatively non-specific manner. To steer the transcription of viral RNA into viral proteins , for example, N must, however, equally be able to recognize specific positions on the viral RNA, called RNA motifs.
Researchers led by Dr. Sophie Korn and Dr. Andreas Schlundt from the Institute for Molecular Biosciences and the Center for Biomolecular Magnetic Resonance at Goethe University Frankfurt have now shed light on exactly how this specific binding through one of N's tools, known as the N-terminal domain , works. Their results build on preliminary studies by the COVID19-NMR consortium established in Frankfurt during the pandemic.
Belgique Dernières Nouvelles, Belgique Actualités
Similar News:Vous pouvez également lire des articles d'actualité similaires à celui-ci que nous avons collectés auprès d'autres sources d'information.
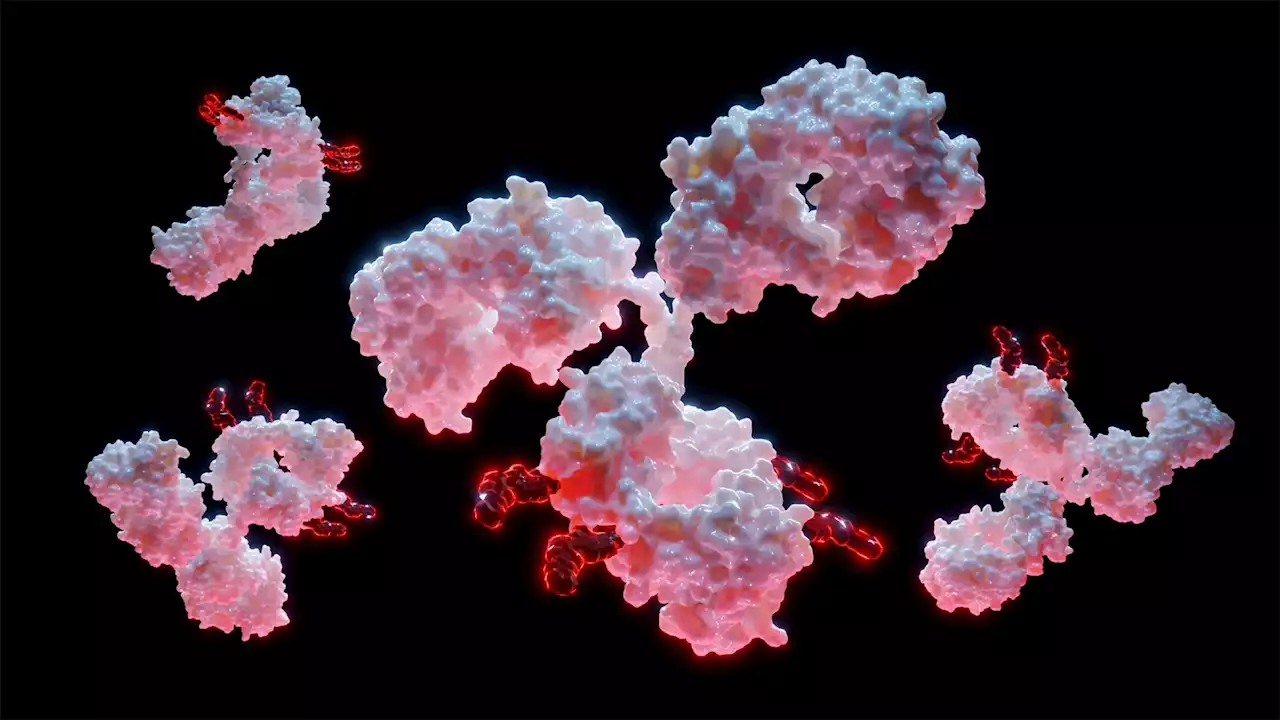 A hybrid approach to re-engineer a SARS-CoV-1 neutralizing antibody against SARS-CoV-2A hybrid approach involving a combination of conventional discovery and antibody repurposing to combat COVID-19.
A hybrid approach to re-engineer a SARS-CoV-1 neutralizing antibody against SARS-CoV-2A hybrid approach involving a combination of conventional discovery and antibody repurposing to combat COVID-19.
Lire la suite »
 Review shows COVID-19 vaccines are effective against severe cases in childrenCOVID-19 vaccines are effective against severe cases of the disease in children and adolescents, according to a review. However, with most children now having caught the SARS-CoV-2 virus and building up a natural immunity, the additional benefit of vaccination in healthy children is minimal.
Review shows COVID-19 vaccines are effective against severe cases in childrenCOVID-19 vaccines are effective against severe cases of the disease in children and adolescents, according to a review. However, with most children now having caught the SARS-CoV-2 virus and building up a natural immunity, the additional benefit of vaccination in healthy children is minimal.
Lire la suite »
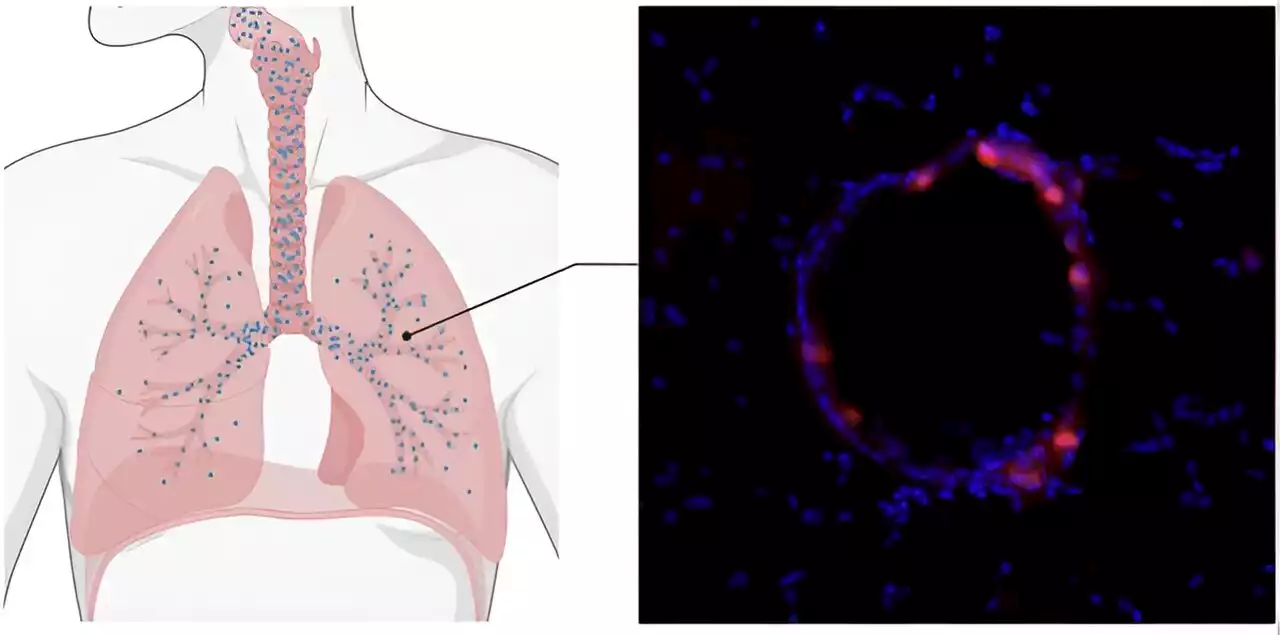 An mRNA COVID vaccine (and potentially more) with nanoparticles, no shot neededA team of researchers has developed an inhalable vaccine that successfully protects against the COVID virus. It also opens the door to delivering other messenger RNA (mRNA) therapeutics for gene replacement therapy and other treatments in the lungs.
An mRNA COVID vaccine (and potentially more) with nanoparticles, no shot neededA team of researchers has developed an inhalable vaccine that successfully protects against the COVID virus. It also opens the door to delivering other messenger RNA (mRNA) therapeutics for gene replacement therapy and other treatments in the lungs.
Lire la suite »
 Four CT residents test positive for Powassan virusFour Connecticut residents have tested positive for Powassan virus, according to the state Department of Public Health. The four cases are the first to be identified in the state this year. Two men who are 60 years old and up from Middlesex County and Litchfield County became ill in early July. Two women who are 50 years old and up…
Four CT residents test positive for Powassan virusFour Connecticut residents have tested positive for Powassan virus, according to the state Department of Public Health. The four cases are the first to be identified in the state this year. Two men who are 60 years old and up from Middlesex County and Litchfield County became ill in early July. Two women who are 50 years old and up…
Lire la suite »
 'I watched my baby die in my arms after he caught a common virus'Georgia Hoad says her baby appeared happy and healthy at first
'I watched my baby die in my arms after he caught a common virus'Georgia Hoad says her baby appeared happy and healthy at first
Lire la suite »
 Covid warning symptoms for each of the new strains detected worldwideHealth experts are warning that cases of the virus are on the rise once again.
Covid warning symptoms for each of the new strains detected worldwideHealth experts are warning that cases of the virus are on the rise once again.
Lire la suite »