\n\t\t\tKeep abreast of significant corporate, financial and political developments around the world.\n\t\t\tStay informed and spot emerging risks and opportunities with independent global reporting, expert\n\t\t\tcommentary and analysis you can trust.\n\t\t
During your trial you will have complete digital access to FT.com with everything in both of our Standard Digital and Premium Digital packages.
Standard Digital includes access to a wealth of global news, analysis and expert opinion. Premium Digital includes access to our premier business column, Lex, as well as 15 curated newsletters covering key business themes with original, in-depth reporting. For a full comparison of Standard and Premium Digital,Change the plan you will roll onto at any time during your trial by visiting the “Settings & Account” section.
You may also opt to downgrade to Standard Digital, a robust journalistic offering that fulfils many user’s needs. Compare Standard and Premium DigitalAny changes made can be done at any time and will become effective at the end of the trial period, allowing you to retain full access for 4 weeks, even if you downgrade or cancel.
Belgique Dernières Nouvelles, Belgique Actualités
Similar News:Vous pouvez également lire des articles d'actualité similaires à celui-ci que nous avons collectés auprès d'autres sources d'information.
 Excess deaths by sex and Age Group in the first two years of the COVID-19 pandemic in the United States - Health Care Management ScienceThe COVID-19 pandemic hastened hundreds of thousands of deaths in the United States. Many of these excess deaths are directly attributed to COVID-19, but others stem from the pandemic’s social, economic, and health care system disruptions. This study compares provisional mortality data for age and sex subgroups across different time windows, with and without COVID-19 deaths, and assesses whether mortality risks are returning to pre-pandemic levels. Using provisional mortality reports from the CDC, we compute mortality risks for 22 age and sex subgroups in 2021 and compare against 2015–2019 using odds ratios. We repeat this comparison for the first twelve full months of the COVID-19 pandemic in the United States (April 2020–March 2021) against the next twelve full months (April 2021–March 2022). Mortality risks for most subgroups were significantly higher in 2021 than in 2015–2019, both with and without deaths involving COVID-19. For ages 25–54, Year 2 (April 2021–March 2022) was more fatal than Year 1 (April 2020–March 2021), whereas total mortality risks for the 65 + age groups declined. Given so many displaced deaths in the first two years of the COVID-19 pandemic, mortality risks in the next few years may fall below pre-pandemic levels. Provisional mortality data suggest this is already happening for the 75 + age groups when excluding COVID-19 deaths.
Excess deaths by sex and Age Group in the first two years of the COVID-19 pandemic in the United States - Health Care Management ScienceThe COVID-19 pandemic hastened hundreds of thousands of deaths in the United States. Many of these excess deaths are directly attributed to COVID-19, but others stem from the pandemic’s social, economic, and health care system disruptions. This study compares provisional mortality data for age and sex subgroups across different time windows, with and without COVID-19 deaths, and assesses whether mortality risks are returning to pre-pandemic levels. Using provisional mortality reports from the CDC, we compute mortality risks for 22 age and sex subgroups in 2021 and compare against 2015–2019 using odds ratios. We repeat this comparison for the first twelve full months of the COVID-19 pandemic in the United States (April 2020–March 2021) against the next twelve full months (April 2021–March 2022). Mortality risks for most subgroups were significantly higher in 2021 than in 2015–2019, both with and without deaths involving COVID-19. For ages 25–54, Year 2 (April 2021–March 2022) was more fatal than Year 1 (April 2020–March 2021), whereas total mortality risks for the 65 + age groups declined. Given so many displaced deaths in the first two years of the COVID-19 pandemic, mortality risks in the next few years may fall below pre-pandemic levels. Provisional mortality data suggest this is already happening for the 75 + age groups when excluding COVID-19 deaths.
Lire la suite »
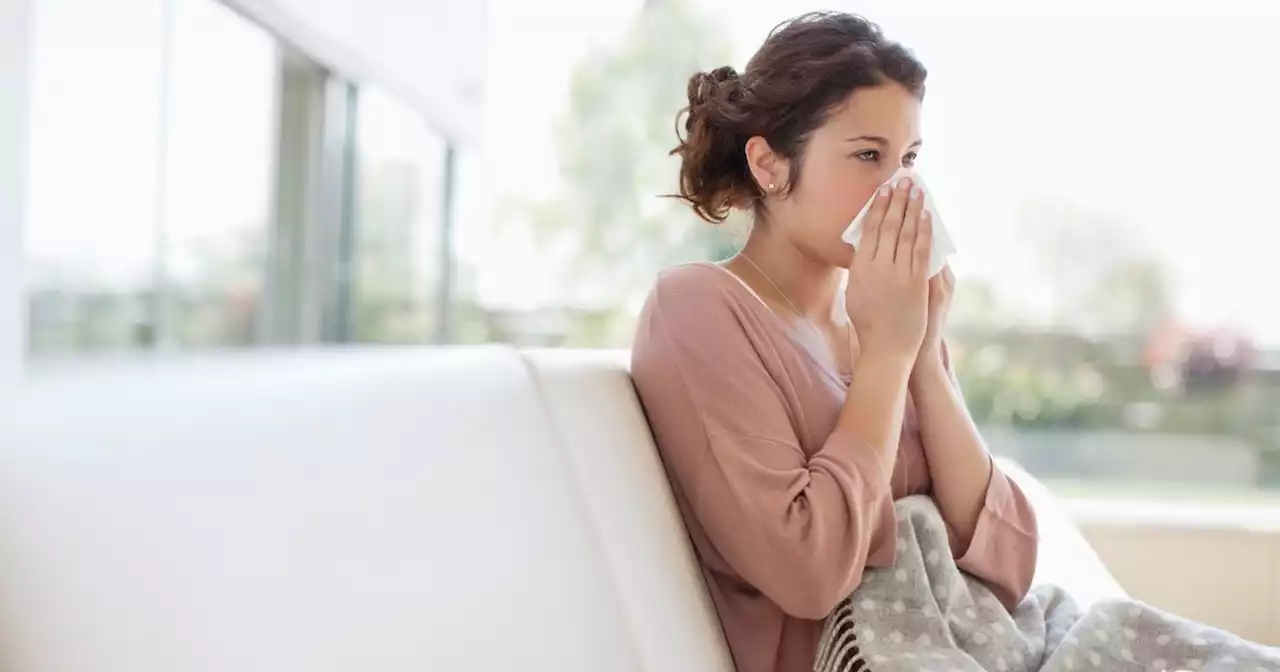 The symptoms and differences between common cold, flu and CovidFlu cases are on the rise earlier than usual this year
The symptoms and differences between common cold, flu and CovidFlu cases are on the rise earlier than usual this year
Lire la suite »
 SSPH+ | The Real-World Impact of Vaccination on COVID-19 Cases During Europe’s Fourth WaveBackground Disease control is important to limit the social, economic and health effects of COVID-19 and reduce the risk of novel variants emerging. Evidence suggests vaccines are less effective against the Omicron variant, but their impact on disease control is unclear. Methods We used a longitudinal fixed effects Poisson regression model to assess the impact of vaccination on COVID-19 case rates across 32 countries in Europe from 13th October to 01st January 2022. We controlled for country and time fixed effects and the severity of public health restrictions. Results Full vaccination coverage increased by 4.2%, leading to a 54% reduction in case rates across Europe (p|0.001). This protection decreased over time but remained significant at five weeks after the detection of Omicron. Mean booster vaccination rates increased from 2.71% to 24.5% but provided no significant additional benefit. For every one-unit increase in the severity of public health restrictions, case rates fell by a further 2% (p=0.019). Conclusions Full vaccination significantly limited the spread of COVID-19 and blunted the impact of the Omicron variant, despite becoming less useful over time.
SSPH+ | The Real-World Impact of Vaccination on COVID-19 Cases During Europe’s Fourth WaveBackground Disease control is important to limit the social, economic and health effects of COVID-19 and reduce the risk of novel variants emerging. Evidence suggests vaccines are less effective against the Omicron variant, but their impact on disease control is unclear. Methods We used a longitudinal fixed effects Poisson regression model to assess the impact of vaccination on COVID-19 case rates across 32 countries in Europe from 13th October to 01st January 2022. We controlled for country and time fixed effects and the severity of public health restrictions. Results Full vaccination coverage increased by 4.2%, leading to a 54% reduction in case rates across Europe (p|0.001). This protection decreased over time but remained significant at five weeks after the detection of Omicron. Mean booster vaccination rates increased from 2.71% to 24.5% but provided no significant additional benefit. For every one-unit increase in the severity of public health restrictions, case rates fell by a further 2% (p=0.019). Conclusions Full vaccination significantly limited the spread of COVID-19 and blunted the impact of the Omicron variant, despite becoming less useful over time.
Lire la suite »
 Study finds risk of seizures is higher after COVID-19 than after influenzaPeople who have a COVID-19 infection are more likely to develop seizures or epilepsy within the next six months than people who have an influenza infection, according to a study published in the November 16, 2022, online issue of Neurology. The increased risk was more noticeable in children than adults. It was also more noticeable in people who did not need hospitalization for COVID-19 infections.
Study finds risk of seizures is higher after COVID-19 than after influenzaPeople who have a COVID-19 infection are more likely to develop seizures or epilepsy within the next six months than people who have an influenza infection, according to a study published in the November 16, 2022, online issue of Neurology. The increased risk was more noticeable in children than adults. It was also more noticeable in people who did not need hospitalization for COVID-19 infections.
Lire la suite »
 Studies provide latest 'real world' evidence on effectiveness of COVID-19 treatmentsTwo studies published by The BMJ today provide up to date evidence on the effectiveness of both currently licensed and possible COVID-19 treatments under everyday ('real world') conditions, helping to shed more light on whether these drugs can prevent people from becoming seriously ill.
Studies provide latest 'real world' evidence on effectiveness of COVID-19 treatmentsTwo studies published by The BMJ today provide up to date evidence on the effectiveness of both currently licensed and possible COVID-19 treatments under everyday ('real world') conditions, helping to shed more light on whether these drugs can prevent people from becoming seriously ill.
Lire la suite »