A new study led by researchers at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai has revealed key differences in gut bacteria and their metabolic byproducts in infants that may predict the development of peanut allergies by mid-childhood. The findings, published online August 22 in the Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, could pave the way for new strategies to prevent or treat this increasingly common food allergy.
and the metabolites they produce between children who did and did not develop a peanut allergy by around age 9.Infants who eventually developed peanut allergies had lower gut microbiome diversity during their early years.
Metabolites associated with peanut allergy development were linked to the"histidine metabolism pathway"—a process in the body that breaks down and uses the protein building block histidine. However, Dr. Bunyavanich also cautioned against drawing premature conclusions, noting,"While it's exciting to think our gut bacteria might influence our risk of developing allergies, it's crucial to note that altering a child's gut bacteria isn't yet an immediate solution. We need further research to truly harness these findings."
Belgique Dernières Nouvelles, Belgique Actualités
Similar News:Vous pouvez également lire des articles d'actualité similaires à celui-ci que nous avons collectés auprès d'autres sources d'information.
 Study shows benefit of traditional Chinese medicine for heart failureThe traditional Chinese medicine qiliqiangxin reduces hospitalization for heart failure and cardiovascular death in patients with heart failure and a reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF), according to late breaking research presented in a Hot Line session today at ESC Congress 2023.
Study shows benefit of traditional Chinese medicine for heart failureThe traditional Chinese medicine qiliqiangxin reduces hospitalization for heart failure and cardiovascular death in patients with heart failure and a reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF), according to late breaking research presented in a Hot Line session today at ESC Congress 2023.
Lire la suite »
 First randomized trial of traditional Chinese medicine for heart failure shows benefitThe traditional Chinese medicine qiliqiangxin reduces hospitalization for heart failure and cardiovascular death in patients with heart failure and a reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF), according to late breaking research presented in a Hot Line session August 26 at ESC Congress 2023.
First randomized trial of traditional Chinese medicine for heart failure shows benefitThe traditional Chinese medicine qiliqiangxin reduces hospitalization for heart failure and cardiovascular death in patients with heart failure and a reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF), according to late breaking research presented in a Hot Line session August 26 at ESC Congress 2023.
Lire la suite »
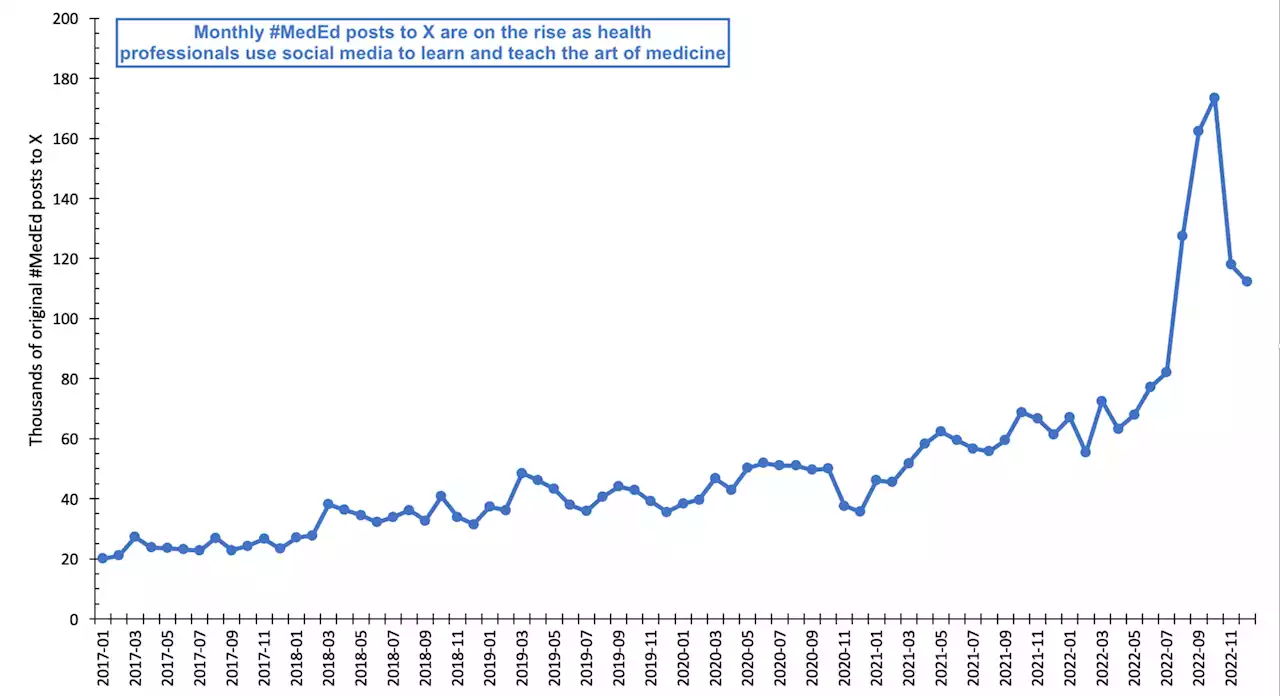 How doctors use social media to advance medicineEver wonder what your doctor is doing on social media? A new study, titled 'MedEd: Medical Education and Knowledge Translation on Social Media,' published in JAMA led by John W. Ayers, Ph.D., from the Qualcomm Institute within the University of California San Diego, finds some physicians are harnessing the reach of social media to share and debate medical advancements.
How doctors use social media to advance medicineEver wonder what your doctor is doing on social media? A new study, titled 'MedEd: Medical Education and Knowledge Translation on Social Media,' published in JAMA led by John W. Ayers, Ph.D., from the Qualcomm Institute within the University of California San Diego, finds some physicians are harnessing the reach of social media to share and debate medical advancements.
Lire la suite »
 Wildfire smoke is an increasing threat to Canadians' health, say researchersAir quality in Canada has improved over the past several decades, and Canada's air is among the cleanest in the world. But that progress is threatened by smoke from wildfires, which are becoming more frequent and more intense with climate change.
Wildfire smoke is an increasing threat to Canadians' health, say researchersAir quality in Canada has improved over the past several decades, and Canada's air is among the cleanest in the world. But that progress is threatened by smoke from wildfires, which are becoming more frequent and more intense with climate change.
Lire la suite »
 Researchers find key for transforming cancer cells to muscle in rhabdomyosarcomaFor six years, Professor Christopher Vakoc's lab at Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory has been on a mission to transform sarcoma cells into regularly functioning tissue cells. Sarcomas are cancers that form in connective tissues such as muscle. Treatment often involves chemotherapy, surgery, and radiation—procedures that are especially tough on kids. If doctors could transform cancer cells into healthy cells, it would offer patients a whole new treatment option—one that could spare them and their families a great deal of pain and suffering.
Researchers find key for transforming cancer cells to muscle in rhabdomyosarcomaFor six years, Professor Christopher Vakoc's lab at Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory has been on a mission to transform sarcoma cells into regularly functioning tissue cells. Sarcomas are cancers that form in connective tissues such as muscle. Treatment often involves chemotherapy, surgery, and radiation—procedures that are especially tough on kids. If doctors could transform cancer cells into healthy cells, it would offer patients a whole new treatment option—one that could spare them and their families a great deal of pain and suffering.
Lire la suite »
 Researchers study barriers and facilitators to accessing health care in rural MissouriRural Missourians often face more disparities in health outcomes than their urban and suburban counterparts, in part from challenges accessing health care—a problem amplified in recent years by a growing physician shortage. But a new study at the University of Missouri found that health and health care organizations are increasingly offering basic social services, such as transportation, housing, food, and mental health support, as they recognize these services contribute to a person's overall health.
Researchers study barriers and facilitators to accessing health care in rural MissouriRural Missourians often face more disparities in health outcomes than their urban and suburban counterparts, in part from challenges accessing health care—a problem amplified in recent years by a growing physician shortage. But a new study at the University of Missouri found that health and health care organizations are increasingly offering basic social services, such as transportation, housing, food, and mental health support, as they recognize these services contribute to a person's overall health.
Lire la suite »
