Inflammation and cancer: Identifying the role of copper paves the way for new therapeutic applications nature
. However, investigation of its mechanism of action is hampered by its poor pharmacology resulting in low potency, which necessitates the administration of high doses. Thus LCC-12—which we rename ‘supformin’—exhibits improved biological and preclinical characteristics over metformin, making it a suitable drug-like small molecule for revealing novel mechanistic features of biguanides.
as a regulator of cell plasticity and unveil a therapeutic strategy based on the control and fine-tuning of epigenetic cell states.Peripheral blood samples were collected from 128 healthy donors at Etablissement Français du Sang . The use of EFS blood samples from anonymous donors was approved by the Institut National de la Santé et de la Recherche Médicale committee. Written consent was obtained from all the donors.
MDMs were activated with LPS and IFNγ and co-treated with ATTM or EDTA , hyaluronate , methylated hyaluronate , LCC-12 , LCC-4,4 , metformin ,-penicillamine , trientine hydrochloride or anti-human CD44 therapeutic antibody for 24 h. aMDMs were treated with CCCP ,C-LCC-12 , LCC-12,4 or trientine alkyne for 3 h, by adding the reagents directly to the media. Dendritic cells were co-treated with LPS and LCC-12 for 24 h. CD4T cells were co-treated with CD3/CD28 and LCC-12 for 48 h.
Belgique Dernières Nouvelles, Belgique Actualités
Similar News:Vous pouvez également lire des articles d'actualité similaires à celui-ci que nous avons collectés auprès d'autres sources d'information.
 Single inhalation exposure to polyamide micro and nanoplastic particles impairs vascular dilation without generating pulmonary inflammation in virgin female Sprague Dawley rats - Particle and Fibre ToxicologyBackground Exposure to micro- and nanoplastic particles (MNPs) in humans is being identified in both the indoor and outdoor environment. Detection of these materials in the air has made inhalation exposure to MNPs a major cause for concern. One type of plastic polymer found in indoor and outdoor settings is polyamide, often referred to as nylon. Inhalation of combustion-derived, metallic, and carbonaceous aerosols generate pulmonary inflammation, cardiovascular dysfunction, and systemic inflammation. Additionally, due to the additives present in plastics, MNPs may act as endocrine disruptors. Currently there is limited knowledge on potential health effects caused by polyamide or general MNP inhalation. Objective The purpose of this study is to assess the toxicological consequences of a single inhalation exposure of female rats to polyamide MNP during estrus by means of aerosolization of MNP. Methods Bulk polyamide powder (i.e., nylon) served as a representative MNP. Polyamide aerosolization was characterized using particle sizers, cascade impactors, and aerosol samplers. Multiple-Path Particle Dosimetry (MPPD) modeling was used to evaluate pulmonary deposition of MNPs. Pulmonary inflammation was assessed by bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) cell content and H&E-stained tissue sections. Mean arterial pressure (MAP), wire myography of the aorta and uterine artery, and pressure myography of the radial artery was used to assess cardiovascular function. Systemic inflammation and endocrine disruption were quantified by measurement of proinflammatory cytokines and reproductive hormones. Results Our aerosolization exposure platform was found to generate particles within the micro- and nano-size ranges (thereby constituting MNPs). Inhaled particles were predicted to deposit in all regions of the lung; no overt pulmonary inflammation was observed. Conversely, increased blood pressure and impaired dilation in the uterine vasculature was noted while aortic vascular reactivity was un
Single inhalation exposure to polyamide micro and nanoplastic particles impairs vascular dilation without generating pulmonary inflammation in virgin female Sprague Dawley rats - Particle and Fibre ToxicologyBackground Exposure to micro- and nanoplastic particles (MNPs) in humans is being identified in both the indoor and outdoor environment. Detection of these materials in the air has made inhalation exposure to MNPs a major cause for concern. One type of plastic polymer found in indoor and outdoor settings is polyamide, often referred to as nylon. Inhalation of combustion-derived, metallic, and carbonaceous aerosols generate pulmonary inflammation, cardiovascular dysfunction, and systemic inflammation. Additionally, due to the additives present in plastics, MNPs may act as endocrine disruptors. Currently there is limited knowledge on potential health effects caused by polyamide or general MNP inhalation. Objective The purpose of this study is to assess the toxicological consequences of a single inhalation exposure of female rats to polyamide MNP during estrus by means of aerosolization of MNP. Methods Bulk polyamide powder (i.e., nylon) served as a representative MNP. Polyamide aerosolization was characterized using particle sizers, cascade impactors, and aerosol samplers. Multiple-Path Particle Dosimetry (MPPD) modeling was used to evaluate pulmonary deposition of MNPs. Pulmonary inflammation was assessed by bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) cell content and H&E-stained tissue sections. Mean arterial pressure (MAP), wire myography of the aorta and uterine artery, and pressure myography of the radial artery was used to assess cardiovascular function. Systemic inflammation and endocrine disruption were quantified by measurement of proinflammatory cytokines and reproductive hormones. Results Our aerosolization exposure platform was found to generate particles within the micro- and nano-size ranges (thereby constituting MNPs). Inhaled particles were predicted to deposit in all regions of the lung; no overt pulmonary inflammation was observed. Conversely, increased blood pressure and impaired dilation in the uterine vasculature was noted while aortic vascular reactivity was un
Lire la suite »
 Green Choir holding singing sessions at Ingol’s Dobcroft Nature ReserveGreen Choir group at Dobcroft A Green Choir is singing among the trees and reedbeds of Ingol's Dobcroft Nature Reserve. Following a pilot event in March,
Green Choir holding singing sessions at Ingol’s Dobcroft Nature ReserveGreen Choir group at Dobcroft A Green Choir is singing among the trees and reedbeds of Ingol's Dobcroft Nature Reserve. Following a pilot event in March,
Lire la suite »
 Ex vivo drug response heterogeneity reveals personalized therapeutic strategies for patients with multiple myeloma - Nature CancerSnijder and colleagues use ex vivo pharmacoscopy and bone marrow composition profiling in a cohort of patients with multiple myeloma to identify tailored therapeutic sensitivities and stratify the cohort into three microenvironmental PhenoGroups.
Ex vivo drug response heterogeneity reveals personalized therapeutic strategies for patients with multiple myeloma - Nature CancerSnijder and colleagues use ex vivo pharmacoscopy and bone marrow composition profiling in a cohort of patients with multiple myeloma to identify tailored therapeutic sensitivities and stratify the cohort into three microenvironmental PhenoGroups.
Lire la suite »
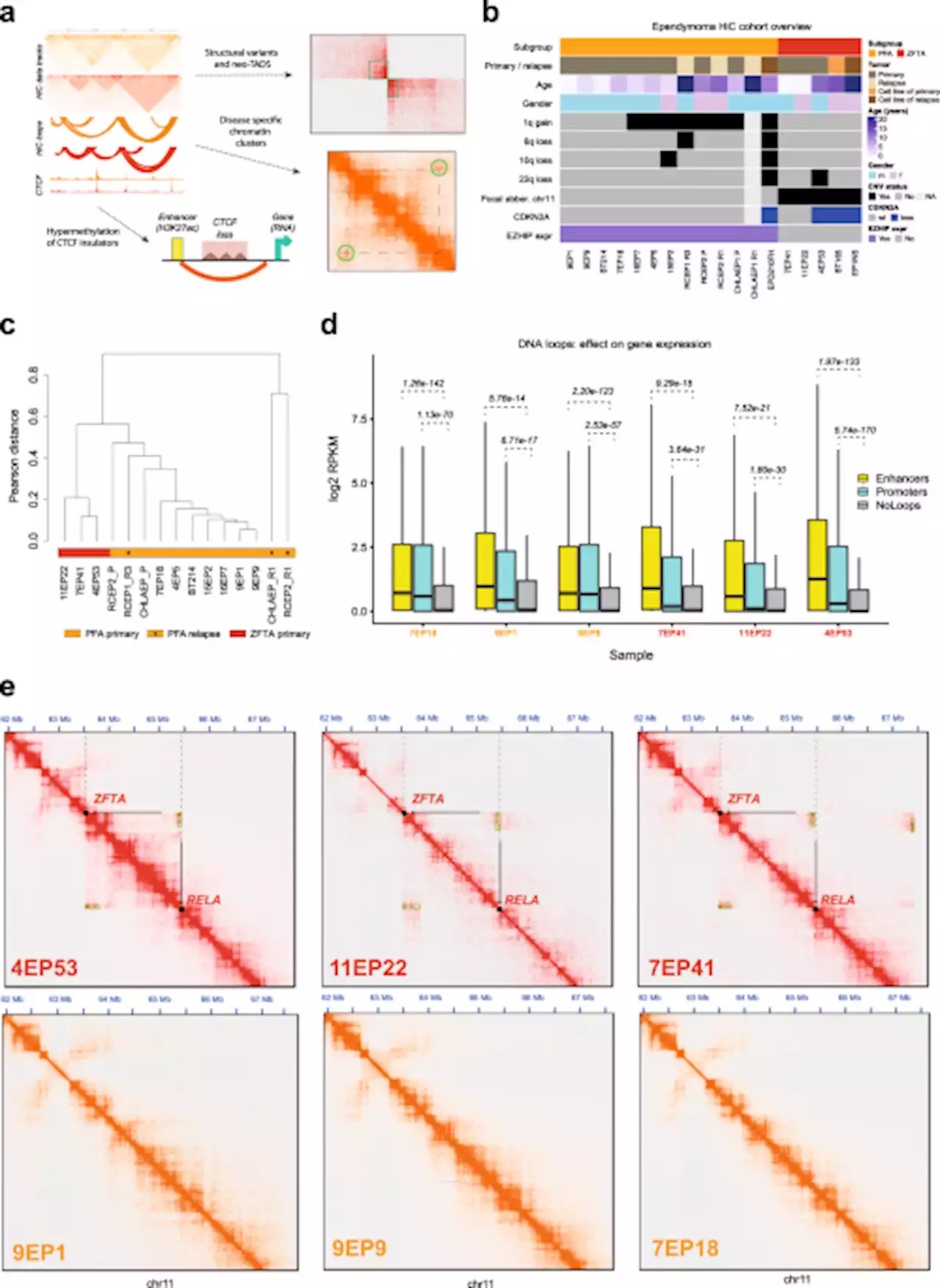 3D genome mapping identifies subgroup-specific chromosome conformations and tumor-dependency genes in ependymoma - Nature CommunicationsEpendymoma is a tumor of the brain or spinal cord with the two most common and aggressive types mainly occurring in children. Here the authors employ 3D genomics and epigenomics to reveal targets for aggressive ependymoma tumors in children.
3D genome mapping identifies subgroup-specific chromosome conformations and tumor-dependency genes in ependymoma - Nature CommunicationsEpendymoma is a tumor of the brain or spinal cord with the two most common and aggressive types mainly occurring in children. Here the authors employ 3D genomics and epigenomics to reveal targets for aggressive ependymoma tumors in children.
Lire la suite »
 Early activation of cellular stress and death pathways caused by cytoplasmic TDP-43 in the rNLS8 mouse model of ALS and FTD - Molecular PsychiatryMolecular Psychiatry - Early activation of cellular stress and death pathways caused by cytoplasmic TDP-43 in the rNLS8 mouse model of ALS and FTD
Early activation of cellular stress and death pathways caused by cytoplasmic TDP-43 in the rNLS8 mouse model of ALS and FTD - Molecular PsychiatryMolecular Psychiatry - Early activation of cellular stress and death pathways caused by cytoplasmic TDP-43 in the rNLS8 mouse model of ALS and FTD
Lire la suite »
 Parents' touching tribute to nature-loving girl, 16, found dead at £44,000 boarding school, as first pictures releasedThe parents of a 16-year-old girl found dead near the grounds of a prestigious all-girls boarding school girl in Buckinghamshire have paid tribute to their daughter, as the first pictures of the student were released.
Parents' touching tribute to nature-loving girl, 16, found dead at £44,000 boarding school, as first pictures releasedThe parents of a 16-year-old girl found dead near the grounds of a prestigious all-girls boarding school girl in Buckinghamshire have paid tribute to their daughter, as the first pictures of the student were released.
Lire la suite »
